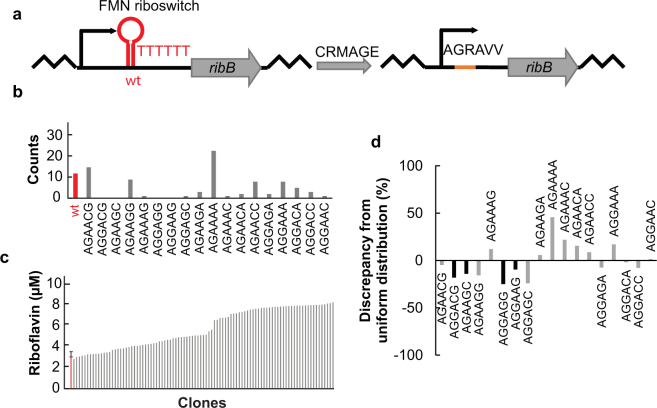
Figure 4.
Genomic integration of a chromosomal 18-members GLOS-RedLibs ribB RBS library and FNM riboswitch removal in an MMR+ strain. (a) Schema of the GLOS-RedLibs ribB RBS library construction. Left: FMN riboswitch and wild type ribB RBS sequence; right: degenerate ribB RBS sequence after GLOS treatment. Note that the riboswitch is supposed to be eliminated concomitantly with the RBS modification step. (b) Library clones were analyzed by Sanger sequencing (n = 96). The 18 possible RBS sequences after genome editing (grey) as well as the wild type context (red) are listed in ascending order of their predicted TIR, except wild type since the TIR including the riboswitch cannot easily be estimated. RBS sequences showing mutations were excluded. Therefore, only 94 of 96 sequenced clones are displayed. (c) Riboflavin production of all isolated RBS library member strains (n = 96, grey, single measurements) compared to wild type (red, in triplicate, mean ± standard deviation). (d) Distribution of sequences in the oligonucleotide pool after chemical synthesis. Illumina-based oligonucleotide pool sequencing for the oligonucleotide used to construct this library. Bars in black indicate oligonucleotides for which no corresponding strains could be recovered during library-based genome editing.