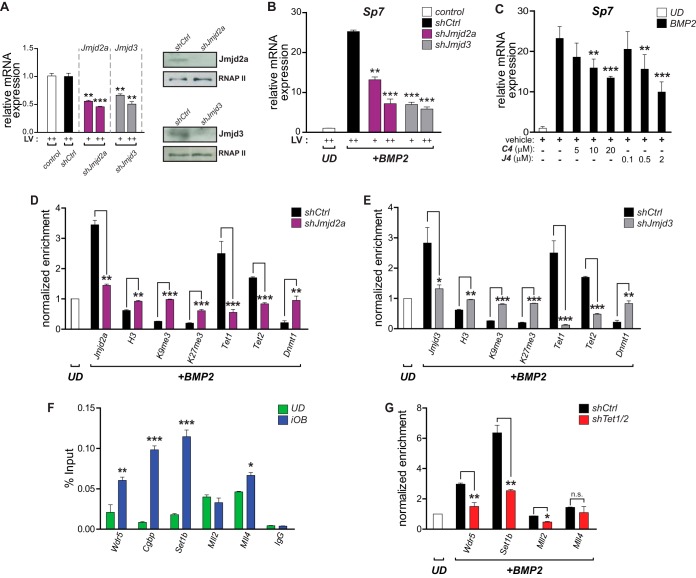
FIG 7.
Coupling of DNA demethylation with H3K4 methylation/H3K9me3 demethylation at the Sp7 promoter during osteoblast differentiation. (A) Demethylases Jmjd2a and Jmjd3 were knocked down in UD cells by infecting the cells with lentiviruses coding for specific shRNAs (shJmjd2a and shJmjd3, respectively). Decreased expression levels of both demethylases were confirmed by RT-qPCR (mRNAs) (left) and Western blotting (proteins) (right). Infection with an unrelated random shRNA (shCtrl) was used as a control. Normalizations were carried out as described in the legend to Fig. 5. (B) Knockdown of Jmjd2a and Jmjd3 impairs Sp7 gene expression during osteoblast differentiation. Infected UD cells were treated with BMP2 for 48 h, and mRNA levels (Sp7 and Gapdh) were determined by RT-qPCR. (C) Treatment of differentiating (iOB) cells with the demethylase inhibitor GSK-J4 (selective for Jmjd3) or C4 (selective for Jmjd2a) inhibits Sp7 mRNA expression in a dose-dependent manner. (D and E) Knockdowns of Jmjd2a (D) and Jmjd3 (E) decrease their presence at the Sp7 promoter and affect the enrichment (measured by ChIP) of histone H3, H3K9me3, H3K27me3, Tet1, Tet2, and Dnmt1 at this promoter sequence. Normalized enrichments are shown as fold changes relative to the values for UD cells. (F) Binding (determined by ChIP) of key components of COMPASS and COMPASS-like complexes to the Sp7 promoter during osteoblast lineage commitment. Enrichment values are shown as a percentage of the input. (G) Tet1/2 knockdown impairs the interaction (determined by ChIP) of the COMPASS complex subunits Wdr5 and Set1b with the Sp7 promoter in iOB cells. In contrast, only minor effects on the binding of Mll2- and Mll4-containing complexes are observed. Results are shown as fold changes relative to the value for UD cells (set as 1). Data represent means ± standard errors of the means (n ≥ 3). *, P ≤ 0.05; **, P ≤ 0.01; ***, P ≤ 0.001 (as determined by Student's t test).