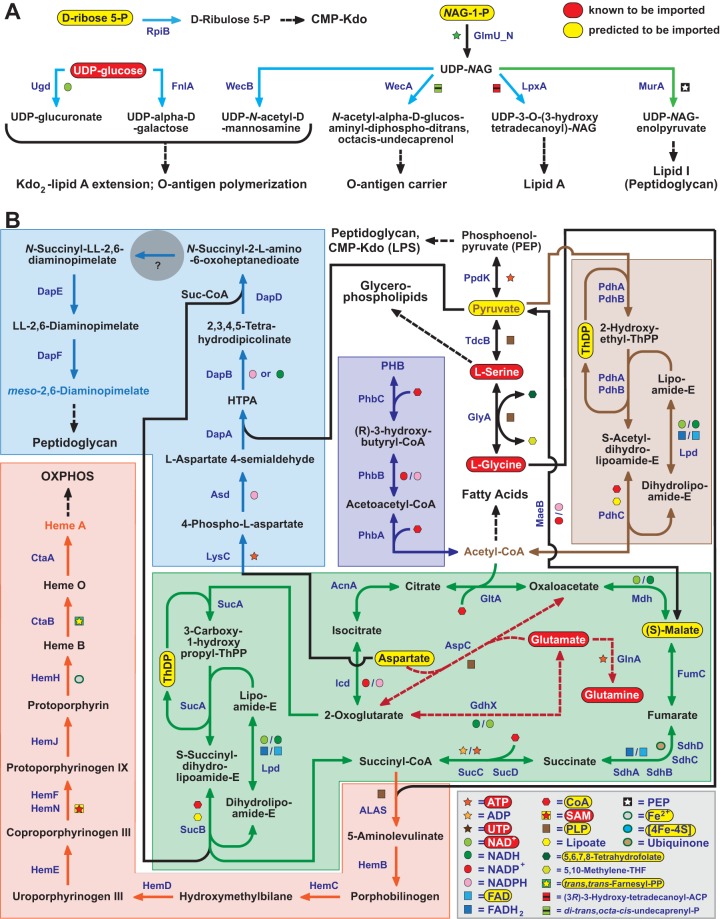
FIG 1 .
Rickettsia species synthesize cell envelope glycoconjugates from imported host sugars and fuel the TCA cycle with a range of host-acquired metabolites. (A) Previously shown to be imported, UDP-glucose is predicted to yield UDP-glucuronate and UDP-α-d-galactose, sugars likely to be used in LPS synthesis (light blue pathway lines). Synthesis of UDP-N-acetyl-d-mannosamine, another sugar likely incorporated into LPS, as well as pathways for O-antigen, lipid A, and lipid I of PGN (green pathway line), initiates with UDP-NAG. Without glycolysis enzymes, rickettsiae are predicted to import host NAG-1-P and convert this charged sugar to UDP-NAG via the uridyltransferase GlmU. d-Ribose 5-P, which is required to initiate CMP-Kdo synthesis, is also predicted to be imported from the host, provided that Rickettsia species lack enzymes of the pentose phosphate pathway. (B) Rickettsia species must acquire pyruvate for generation of PEP and acetyl-CoA. Pyruvate interconversions with Ser, Gly (via Ser), and malate are likely mediated by additional import of these molecules, ensuring that enough pyruvate enters the PDC to yield acetyl-CoA (brown). Aside from entering the TCA cycle (green), acetyl-CoA is also used in fatty acid biosynthesis and production of PHB (dark blue), a storage molecule that is metabolized when host energy sources are unavailable. Imported malate, glutamine (Gln), and glutamate (Glu) likely regulate the flow of acetyl-CoA into the TCA cycle, with Gln/Glu interconversions with 2-oxaloglutarate and oxaloacetate providing additional energy (dashed burgundy pathway lines). Generated aspartate is essential for initiation of the synthesis of DAP, which is used in PGN biosynthesis (light blue), a pathway nearly conserved except for a central hole (gray circle). DAP synthesis also requires generated succinyl-CoA, which is also used to synthesize porphyrins (orange). HTPA, (2S,4S)-4-hydroxy-2,3,4,5-tetrahydrodipicolinate.