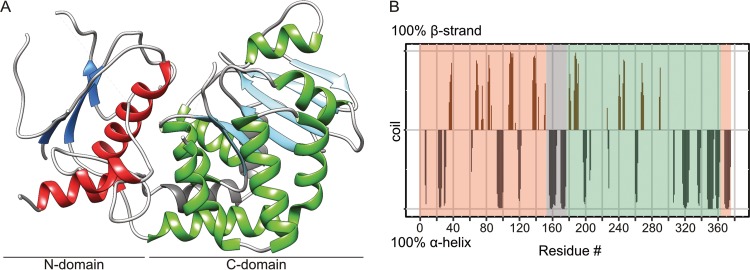
FIG 2 .
EarP folding pattern and topology. (A) Ribbon representation of the 2.3-Å crystal structure of EarPPpu. The illustration was generated with UCSF Chimera (82). Secondary-structure elements are shown, with α-helices in red and green for the N- and C-domains, respectively, and β-strands correspondingly in blue and cyan. The bipartite helix of the linker domain is grey. β-Strand 3, α-helix 5, and short loops with weak electron density are also displayed here but are missing in the PDB coordinate file to improve statistics, as discontinuity in the electron density did not allow proper modeling. (B) Secondary structure of EarP determined by NMR secondary shifts. The secondary structure of individual amino acids is indicated as propensity to form either an α-helix (grey) or a β-strand (brown). The amino acids with a propensity to adopt a random coil or lacking information about secondary structure were assigned zero values in the plot. The propensity values were obtained from Cα, Cβ, NH, and H chemical shifts using TALOS+ (103). The N- and C-terminal EarP domains are boxed in peach and green, respectively. The interconnecting linker is boxed in grey.