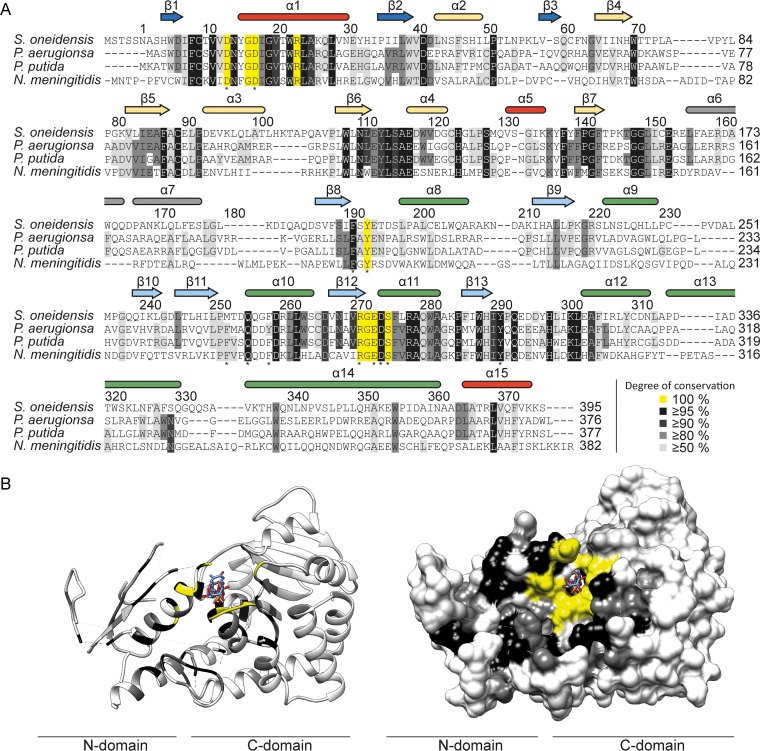
FIG 4 .
Evolutionary conservation of amino acids in EarP homologues. (A) Multiple-sequence alignment of EarP proteins from Shewanella oneidensis, P. aeruginosa, P. putida, and Neisseria meningitidis as a selection from the alignment of 432 protein sequences that were collected from the NCBI database (Data Set S3). The multiple-sequence alignment was generated using Clustal Omega (104). Secondary-structure elements of EarP are shown and based on the EarPPpu crystal structure, NMR analysis, and predictions by MINNOU (105). α-Helices are in red and green for the N- and C-domains, respectively, and β-strands are in blue and cyan. The bipartite helix of the linker domain is grey. Helices and β-strands not resolved in the crystal structure are yellow. Amino acids selected for mutational analysis are indicated by asterisks. (B) The EarPPpu crystal structure was colored according to the degree of conservation of the respective amino acids. Ribbon (left) and surface (right) representations of the EarPPpu crystal structure are shown. Colors indicate the following: yellow, 100%; black, ≥95%; dark grey, ≥90%; light grey, ≥50%; and white, <50% identical residues in all analyzed EarP orthologues. Illustrations were generated with UCSF Chimera (82).