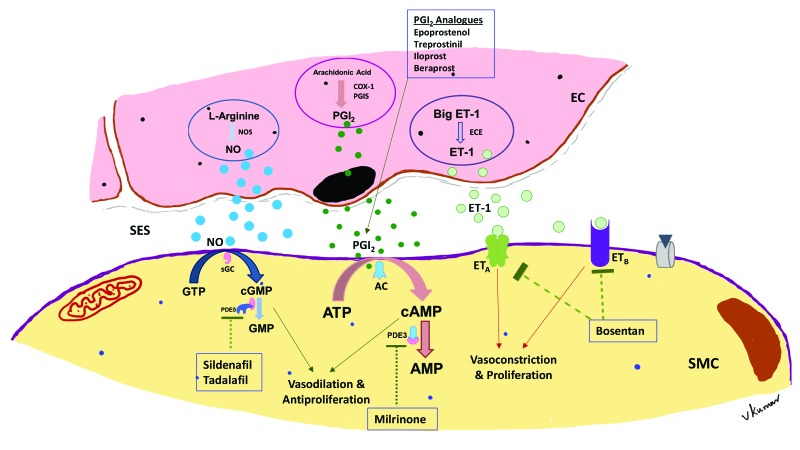
Figure 5.
Schematic diagram of vascular mediators of the lung, their mechanism of action, interaction between the endothelial cell and the smooth muscle cell in the pulmonary vasculature, and its relationship to drugs used in the management of PH in BPD. The three predominant signaling pathways illustrated include: (i) nitric oxide—cGMP system; (ii) PGI2-cAMP system; and (iii) endothelin-1 system. NO: nitric oxide; PGI2: prostacyclin; NOS: nitric oxide synthase; EC: endothelial cell; ET-1: endothelin-1; ECE: endothelin converting enzyme; SES: subendothelial space; SMC: smooth muscle cell; PDE5: phosphodiesterase type 5; PDE3: phosphodiesterase type 3; ETA: endothelin receptor type A; ETB: endothelin receptor type B; AC: adenylate cyclase; sGC: soluble guanylyl cyclase; cGMP: cyclin GMP; COX1: cyclo-oxygenase type 1; PGIS: Prostaglandin synthase