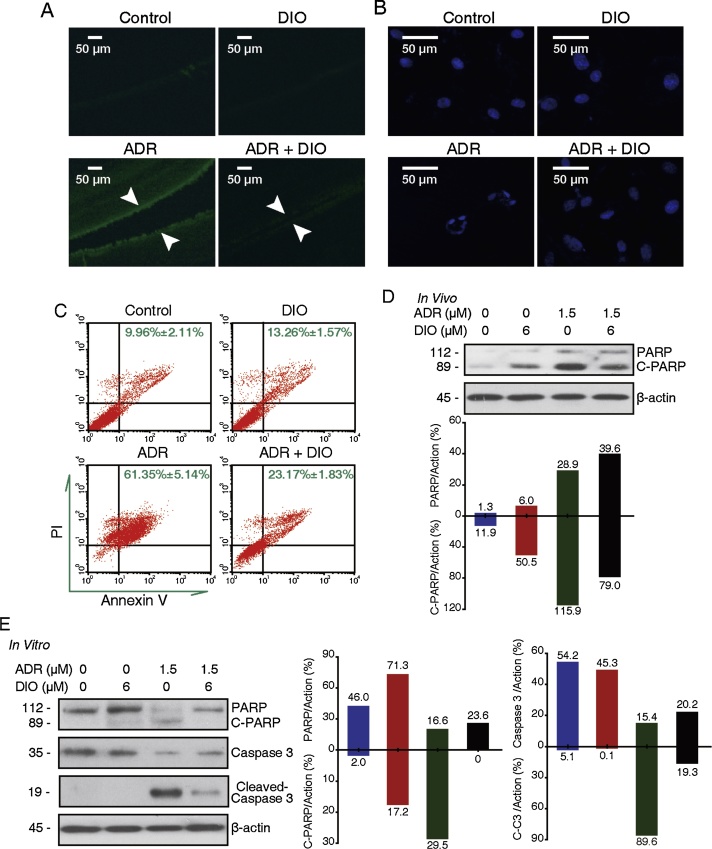
Fig. 2.
DIO attenuates the ADR-induced human retinal pigment epithelium cells apoptosis.
(A) DIO reduced apoptosis in the RPE cells in vivo. The retinal tissues were terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP nick end labelled and were imaged by fluorescent microscopy. The content of TUNEL-positive cells was equal to the number of green points in the photograph. Arrows indicate the thickness of the pigment epithelium layer. (B–C) DIO reduced the apoptosis of RPE cells in vitro. (B) ARPE-19 cells were treated with ADR and DIO for 72 h, and nuclei changes were photographed with fluorescence microscopy. (C) Flow cytometry recording shows the apoptosis rate of the ARPE-19 cells. (D) In vivo, retina extracts were analyzed by western blot analysis after IVI, PARP and cleaved PARP expression were analyzed. (E) In vitro, ARPE-19 cells were treated with drugs for 48 h and whole cell lysates were analyzed by western blot to evaluate the levels of caspase-3, PARP and their cleaved fragments.