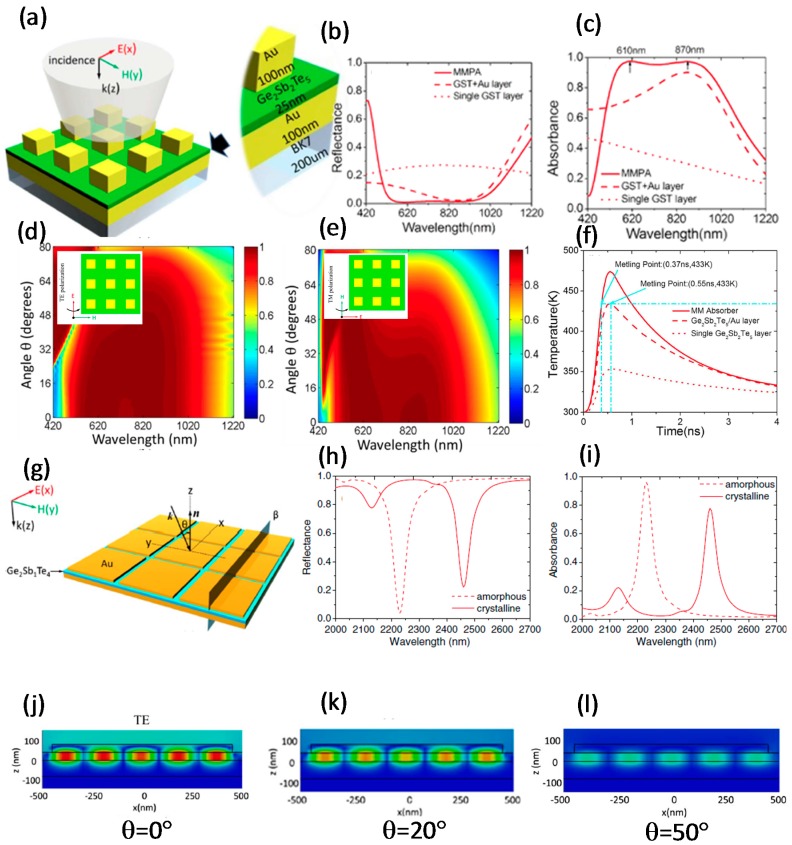
Figure 6.
GST-based tunable absorbers. (a) Structural representation of the broadband absorber with incident light polarization; Simulated spectra of (b) reflectance and (c) absorbance for three configurations including a perfect absorber, hybrid, and single GST layer; Simulated absorbance peak distribution for (d) TE and (e) TM polarization of GST amorphous film; (f) The simulated temperature of one pulse through the perfect absorber, hybrid, and single GST layer; (g) Graphical representation of the absorber structure with the incident light polarization while the incident angle of the plane wave on the surface is θ; Simulated (h) reflectance and (i) absorbance spectra of GST layer at perpendicular incidence; Scattered magnetic field of TE polarization at different angles of (j) θ = 0°, (k) θ = 20°, (l) θ = 50°. (a–f) are adapted from [28], with permission from © 2014 Nature Publishing Group; and (g–l) are adapted from [59], with permission from © 2013 OSA.