Figure EV2. Bioinformatic scheme for determining dfoxo‐dependent and ‐independent protein expression under reduced IIS .
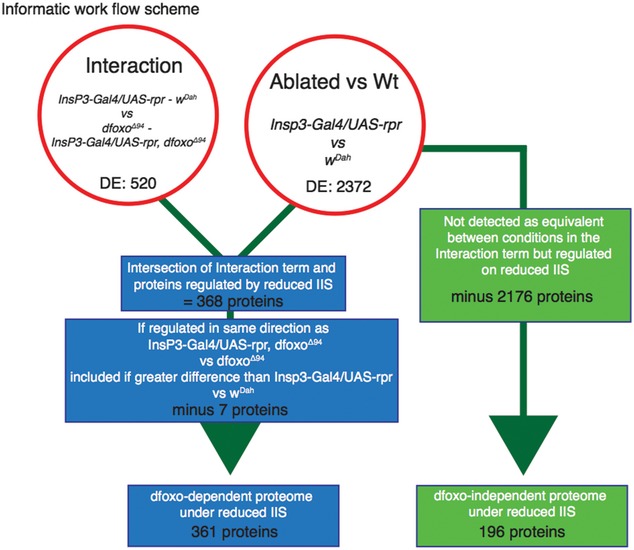
Genotypes defined as w Dah, dfoxo Δ94 mutant, InsP3‐Gal4/UAS‐rpr and InsP3‐Gal4/UAS‐rpr, dfoxo Δ94. Reduced IIS‐mediated changes in the wild‐type background (InsP3‐Gal4/UAS‐rpr vs. w Dah) and in the dfoxo Δ94 background (InsP3‐Gal4/UAS‐rpr, dfoxo Δ94 vs. dfoxo Δ94) or their interaction term (InsP3‐Gal4/UAS‐rpr ‐ w Dah) vs. InsP3‐Gal4/UAS‐rpr, dfoxo Δ94‐dfoxo Δ94. dfoxo‐dependent proteins were defined as proteins regulated between InsP3‐Gal4/UAS‐rpr and w Dah and within the interaction term (InsP3‐Gal4/UAS‐rpr ‐ w Dahvs. InsP3‐Gal4/UAS‐rpr, dfoxo Δ94‐dfoxo Δ94), but also if the expression response was the same in InsP3‐Gal4/UAS‐rpr vs. w Dah and InsP3‐Gal4/UAS‐rpr, dfoxo Δ94 vs. dfoxo Δ94 providing the response was greater in InsP3‐Gal4/UAS‐rpr vs. w Dah. Proteins were identified as dfoxo‐independent if they were regulated between InsP3‐Gal4/UAS‐rpr and w Dah, and were not subject to interaction effects (equivalence given a tissue‐specific threshold). Also included were proteins with a stronger same directional response in InsP3‐Gal4/UAS‐rpr, dfoxo Δ94 vs. dfoxo Δ94 than in InsP3‐Gal4/UAS‐rpr vs. w Dah, regardless of interaction. See Materials and Methods section for full descriptions.
