Figure 20.
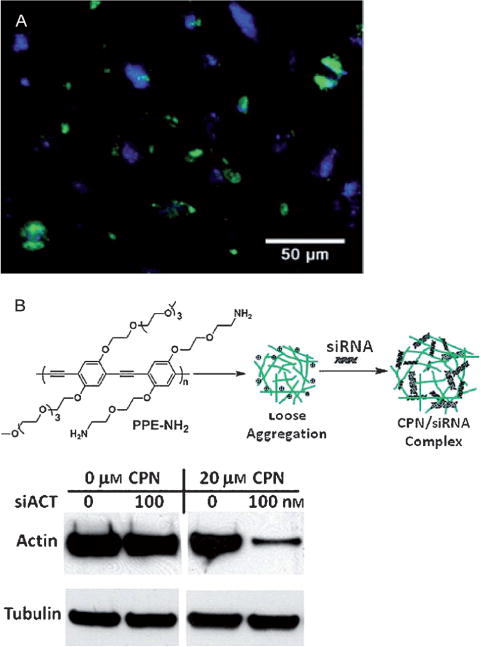
Conjugated polymer nanoparticles for gene delivery. A) Lipid-modified cationic PFPL nanoparticles for delivery of pCX-EGFP plasmids encoding the GFP. Fluorescence imaging of A549 cells after incubation with PFPL/pCX-EGFP nanoparticles showed both blue fluorescence from PFPL and green fluorescence from GFP, thus indicating the PFPL nanoparticles successfully delivered plasmids into cells. Reproduced from Ref. [92] with permission. B) Loosely aggregated PPE nanoparticles for delivery of siRNA. The top shows a schematic illustration of loosely aggregated PPE particles complexed with siRNA. The bottom shows Western blots of actin B (target) and tubulin (control). Significant reduction in the target protein was observed from the CPN/siACT transfection. Actin B expression decreased about 94% under the transfection conditions. Reproduced from Ref. [85] with permission.
