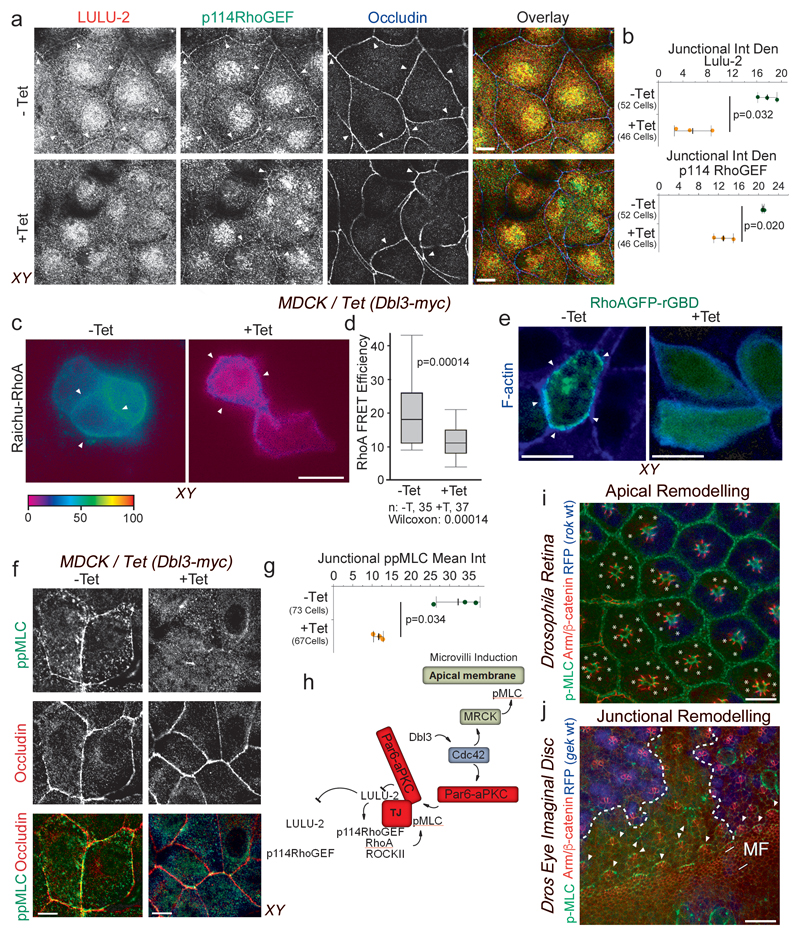
Figure 6. Apical activation of Cdc42 by Dbl3 antagonizes junctional RhoA-stimulated Myosin-II activation.
(a,b) Conditional tetracycline-induced expression of Dbl3 in MDCK cells stimulates loss of junctional RhoA signalling components p114RhoGEF and LULU-2. Shown are confocal xy and z-sections. Junctions are indicated by white arrowheads. (c,d) FRET analysis of RhoA activity in MDCK cells conditionally expressing Dbl3-myc (white arrowheads indicate cell-cell contacts) (e) Confocal analysis of MDCK cells transiently expressing the active RhoA binding domain of rhotekin fused to GFP (GFP-rGBD), conditionally expressing Dbl3-myc (white arrowheads indicate cell-cell junctions). (f,g) Confocal analysis of junctional pMLC activity in MDCK cells conditionally expressing Dbl3-myc. (i) Confocal sections of a Drosophila retina showing wild type cells (blue) and cells mutant for the RhoA effector null allele rok2 (white asterisks) that were stained for pMLC and Armadillo (Arm), the orthologue of mammalian β-catenin. White asterisks indicate rok2-mtant cells. (j) Maximum intensity projection of confocal sections of a mosaic Drosophila eye imaginal disc showing wild type cells (blue nuclei) and cells mutant for gekNP5192 and stained for Armadillo (Arm) and pMLC (MF, morphogenetic furrow; the dashed white lines indicate the borders between wild type and mutant cells; arrowheads point to Myosin-II-rich cell junctions). The schematic diagram illustrates the generation of apically polarized actomyosin activation by apical activation of MRCK and inactivation of junctional RhoA signalling by aPKC. Quantifications show shown are (d) box blots (25th to 75th percentiles, with a line at the median; whiskers extend to the max/min data points; n=35 cells -Tet and n=37 cells +Tet; p value was calculated with a Wilcoxon test), or (b, d, g) based on n=3 independent experiments and showing the data points, means ± 1 SD (in black), the total number of cells analysed for each type of sample across all experiments, and p-values derived from t-tests. Scale bars: 10 μm.