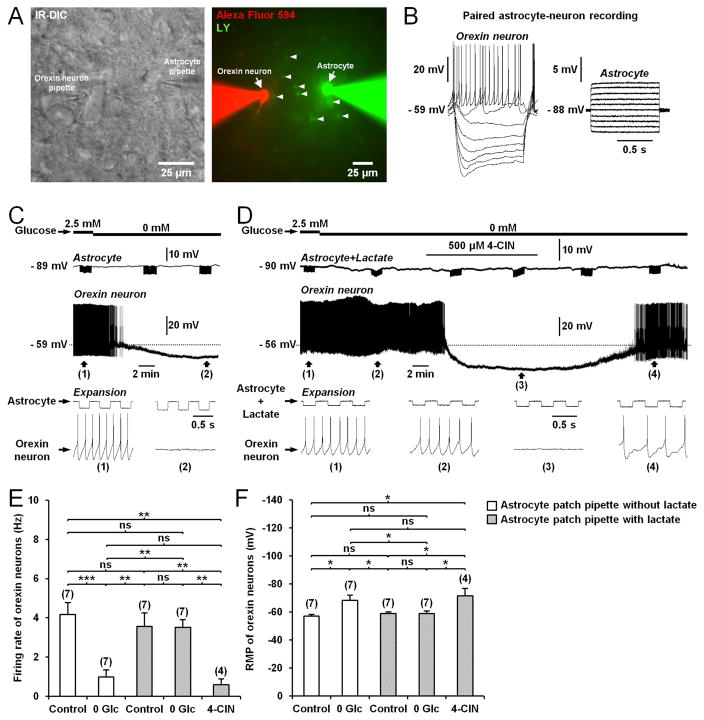
Figure 4. Lactate supply through the astrocytic network sustains the activity of orexin neurons during glucose deprivation.
(A) Left: Infrared differential interference contrast (IR-DIC) image of a paired astrocyte-orexin neuron whole-cell recording in the LHA from Cx43f/f mouse. Right: Fluorescence image of the orexin neuron-astrocyte pair shown in the left picture, filled through the pipette with Alexa Fluor 594 (red) and Lucifer yellow (LY, green), respectively. Note the diffusion of LY to neighboring astrocytes (arrowheads). (B) Responses of the cells recorded in (A) to current pulses from −60 to 10pA (1s, 10pA steps) for the orexin neuron and from −200 to 250pA (1s, 50pA steps) for the astrocyte. (C) Representative paired astrocyte-neuron recording from Cx43f/f mouse showing that glucose deprivation inhibits the orexin neuron firing rate. Downward deflections in the astrocyte trace are membrane potential responses to current pulses (−100pA at 2Hz for 80s) to monitor input resistance. (D) Intracellular delivery of lactate (5mM) to astrocyte (Astrocyte+Lactate) through the patch pipette for at least 20min prevents the inhibitory effect of glucose deprivation on the orexin neuron firing rate. This preventive effect was abolished by bath application of 4-CIN. (E and F) Average firing frequency (E) and resting membrane potential (RMP; F) of orexin neurons from Cx43f/f mice exposed to different conditions (during patch-clamp recording of astrocyte not filled with lactate: in 2.5mM glucose (Control), n=7 cells, 5 mice; in 0mM glucose (0 Glc), n=7 cells, 5 mice; during patch-clamp recording of astrocyte filled with 5mM lactate: in 2.5mM glucose (Control), n=7 cells, 4 mice; in 0mM glucose (0 Glc), n=7 cells, 4 mice; in 500μM 4-CIN, n=4 cells, 4 mice; ANOVA followed by post-hoc test, *p<0.05, **p<0.01 and ***p<0.001; ns, nonsignificant).