Fig. 4.
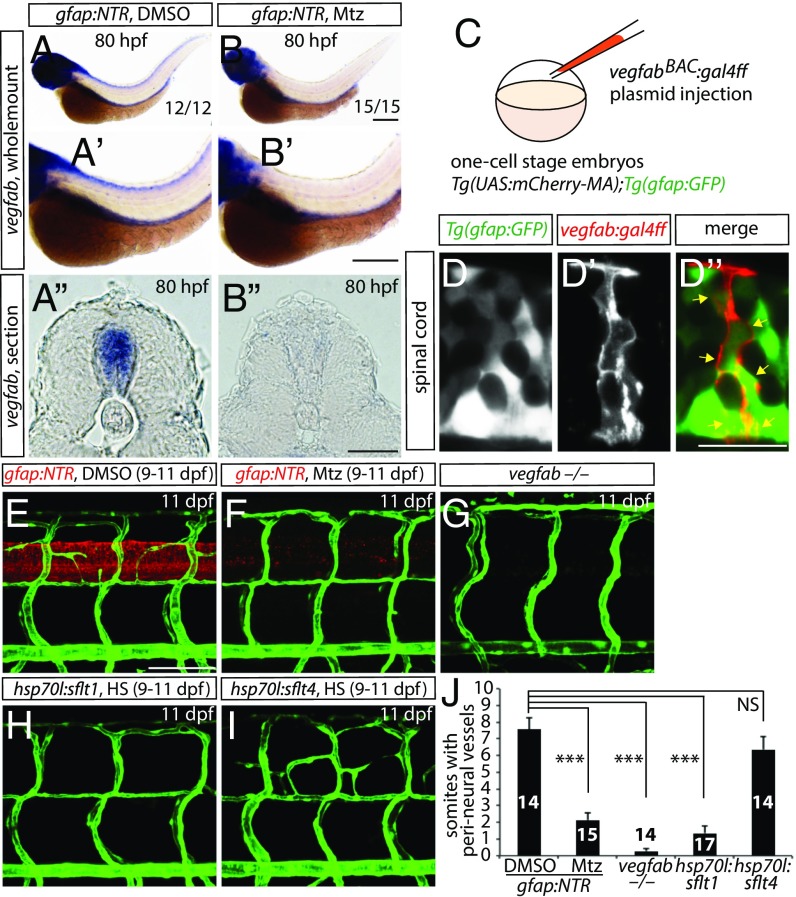
vegfab is expressed by radial glia, and radial glia-ablated fish as well as vegfab mutants fail to develop a PNVP around the spinal cord. (A and B) Whole-mount in situ hybridization for vegfab expression in 80 hpf Tg(gfap:NTR) larvae treated with DMSO (A) or Mtz (B) starting at 30 hpf. High-magnification images of the trunk regions and their cryosections are shown in (A′ and B′) and (A″ and B″), respectively. Mtz-treated fish show decreased vegfab transcripts in the spinal cord compared with DMSO-treated fish. (C) Schematic diagram of the plasmid injection experiments (D–D″). (D–D″) 105 hpf Tg(UAS:mcherry-MA);Tg(gfap:GFP) trunk of fish injected with the vegfab BAC plasmid that drives Gal4ff. Injection of the plasmid drives mCherry expression in cells within the spinal cord (D′), which are also positive for Tg(gfap:GFP) expression (D). Most mCherry+ cells are also GFP+ (D″, yellow arrows). (E–I) 11 dpf Tg(gfap:NTR) trunk vasculature after treatment with DMSO (E) or Mtz (F) starting at 9 dpf; 11 dpf TgBAC(etv2:EGFP) vegfab−/− (G), Tg(kdrl:EGFP);Tg(hsp70l:sflt1) (H), and Tg(kdrl:EGFP);Tg(hsp70l:sflt4) (I) trunk vasculature after heat shocks (H and I). DMSO-treated control fish display vessels that emerge between dorsal ISVs around the spinal cord; however, vessel formation is severely impaired in radial glia-ablated larvae as well as in vegfab−/− animals. Overexpression of sFlt1 also blocked PNVP formation. (J) Quantification of the average number of somites with peri-neural blood vessels (10 somites examined per animal). Values represent means ± SEM, ***P < 0.001. (Scale bars, 200 µm in B–B″, 100 µm in E, and 20 µm in D″.)