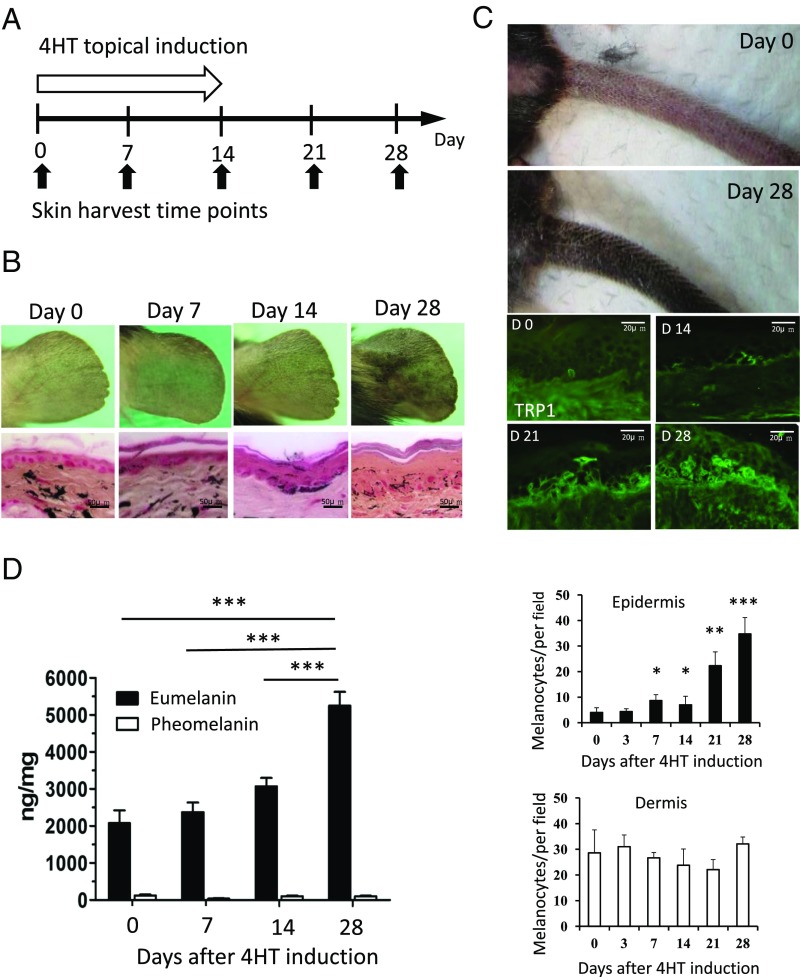
Fig. 2.
CK1α ablation in keratinocytes increased epidermal melanocyte number and eumelanin production. (A and B) Topical treatment with 4HT for 14 d induces skin hyperpigmentation on the ear. Fontana–Masson staining shows increased epidermal thickness and melanin content in the epidermis. (C) Topical treatment with 4HT for 14 d induces skin hyperpigmentation on the tail. TRP1 staining highlights the increased number of melanocytes in the tail epidermis. Quantitation of melanocyte staining shows that the number of dermal melanocytes was not significantly changed. (D) The amount of eumelanin is increased, but pheomelanin remains unchanged during CK1α inhibition. Data are shown as means ± SD; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001.