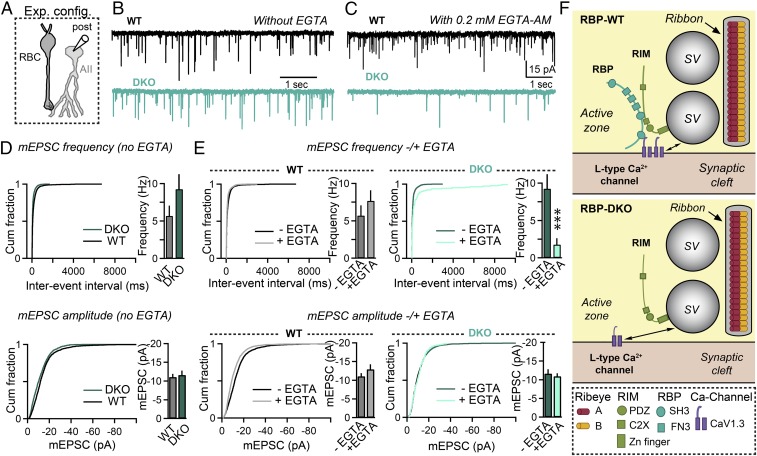
Fig. 8.
Deletion of RBPs alters the sensitivity of quantal release to the slow Ca2+ buffer EGTA at rod bipolar cell to AII amacrine cell synapses. (A) Schematic of the recording configuration. (B and C) Spontaneous mEPSCs recorded from AII amacrine cells in RBP WT (black) and RBP mutant (blue) retinas, without external EGTA-AM (B) or in the presence of 0.2 mM EGTA-AM in the external solution (C). All these experiments were performed in the presence of GABAA receptor blockers. (D) Summary graphs of mEPSC frequency (Top) and mEPSC amplitude (Bottom) in RBP control (black) and RBP mutant (blue) retinas without EGTA-AM in the external solution. Number of experiments: RBP WT, 10 cells; RBP DKO, nine cells. (E) Summary graphs of mEPSC frequency (Top) and mEPSC amplitude (Bottom) in RBP control and RBP mutant retinas before (dark traces) and after (light traces) incubation with 0.2 mM EGTA-AM for 45 min. Number of experiments: RBP WT, nine cells; RBP DKO, nine cells. (F) Model summarizing the effects of deleting RBPs on the structure and function of retina ribbon synapses. All summary graphs are mean ± SD. Statistical analyses for data displayed in bar graphs were performed by Student’s t test, comparing RBP DKO with RBP WT, whereas statistical analyses for data displayed in cumulative distribution plots were performed by K-S test (***P < 0.001; n.s., nonsignificant).