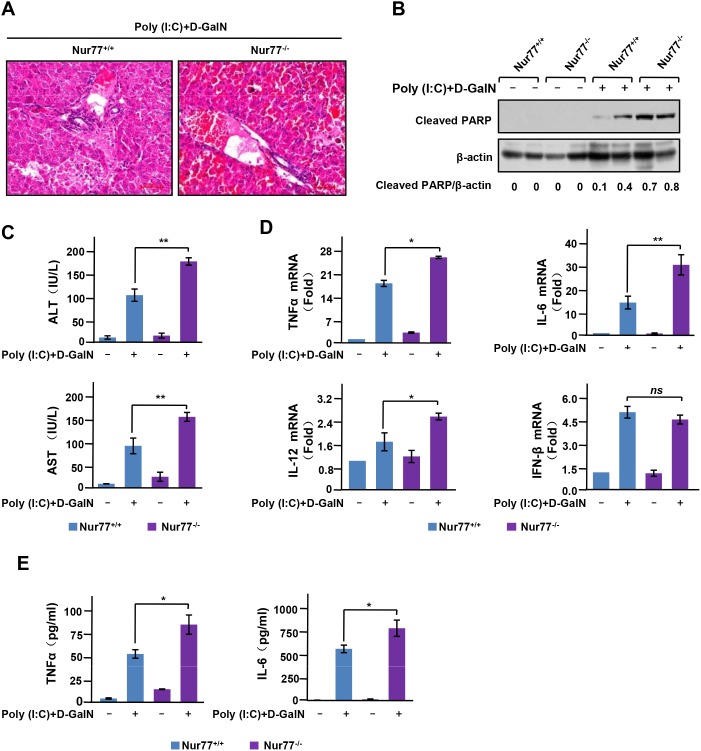
Figure 1. Nur77 attenuates poly (I:C)-induced acute liver inflammation.
(A) H&E staining of liver from Nur77+/+ and Nur77−/− mice 5 h after injection of poly (I:C) (6.25 mg/kg) and D-GalN (0.5 g/kg). Representative images are shown. Scale bars, 100 μM. Original magnification, × 100. (B) Liver extracts were examined by Western blot analysis with antibody to cleaved PARP. Western blot analyses were quantified via densitometry, and the mean ratios of the indicated protein from three independent experiments are shown at the bottom of the figure. (C) ELISA assay of serum transaminase activity at 5 h after injection of poly (I:C)/D-GalN in Nur77+/+ and Nur77−/− mice. Error bars represent mean ± s.d. *p < 0.05. (D) Expression of TNFα, IL-6, IL-12 and IFN-β mRNA was assessed by qPCR in the livers of Nur77+/+ and Nur77−/− mice 3 h after treatment with poly (I:C)/D-GalN. Error bars represent mean ± s.d. from n=3 biological replicates. *P < 0.05. (E) ELISA of the production of TNFα and IL-6 in serum from Nur77+/+ and Nur77−/− mice after intraperitoneal injection of poly (I:C)/D-GalN for 5 hours. *P < 0.05.