Figure 4. Combination of betulinic acid (BA) and chidamide (CDM) synergistically potentiates ROS formation, DNA damage and apoptosis, while SOD2 overexpression diminishes this effect.
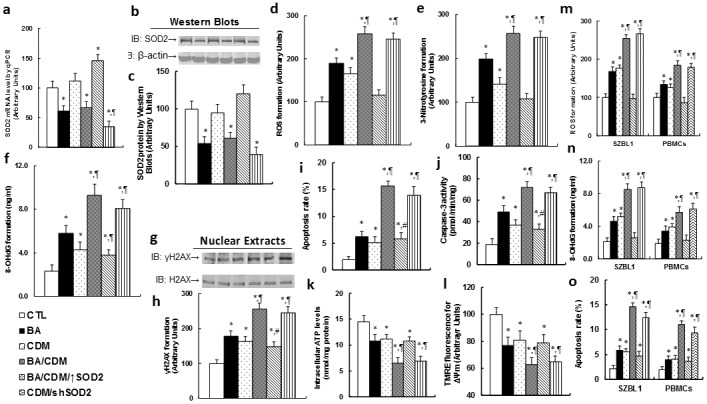
(a-l) The EBV-transformed LCL cells were treated with the control (CTL) alone, 15μg/ml BA alone (BA), 3μM CDM alone (CDM), a combination of BA and CDM (BA/CDM), a combination of BA and CDM treatment in SOD2 overexpression cells (BA/CDM/↑SOD2), or CDM treatment in SOD2 knockdown cells (CDM/shSOD2) for 24 hours, and the cells were harvested for further analysis. (a) SOD2 mRNA level by qPCR, n=4. (b) Representative picture of Western Blots. (c) SOD2 protein quantitation for (b), n=5. (d) ROS formation, n=5. (e) 3-Nitrotyrosine formation, n=5. (f) 8-OHdG formation, n=5. (g) Representative pictures for γH2AX formation. (h) Protein quantitation for (g), n=5. (i) Apoptosis rate by TUNEL assay, n=5. (j) Caspase-3 activity, n=5. (k) Intracellular ATP level, n=5. (l) ∆ᴪ m by TMRE fluorescence, n=5. (m-o) EBV-negative tumor cell line SZBL1 and PBMCs were treated as mentioned in (a) and then harvested for further analysis. (m) ROS formation, n=5. (n) 8-OHdG formation, n=5. (o) Apoptosis rate by TUNEL assay, n=5. *, P<0.05, vs CTL group; ¶, P<0.05, vs BA group; #, P<0.05, vs BA/CDM group. Results are expressed as mean ± SEM.
