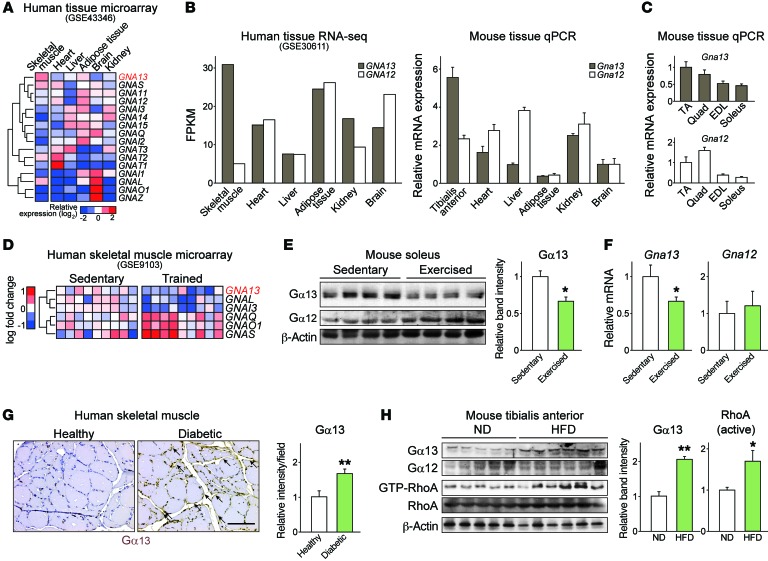
Figure 1. Skeletal muscle Gα13 expression correlates with metabolic alterations.
(A) Tissue distribution of Gα (GNA) subunits in microarray and RNA-seq experiments using human tissues. The data were extracted from GEO GSE10347 and GSE30611. FPKM, fragments per kilobase of transcript per million mapped reads. (B and C) qPCR analysis of Gα13 in mouse tissues. C57BL/6 mice were fasted overnight prior to sacrifice (n = 3 each). Different sets of mice were used in B and C. TA, tibialis anterior; EDL, extensor digitorum longus; Quad, quadriceps. (D) Relative expression of Gα subunits in human quadriceps before or after exercise. Data were extracted from GEO GSE9103. (E and F) Levels of Gα13 protein (E) and transcripts (F) in soleus muscle before and 4 hours after 1 hour of exercise (n = 4 each). (G) Immunostaining for Gα13 in skeletal muscles of a healthy volunteer and a diabetic patient. Scale bar: 100 μm. (H) Immunoblots for Gα13 and GTP-bound RhoA in tibialis anterior muscles from mice fed a normal diet (ND) or a HFD for 13 weeks (n = 5–6 each). For E and H, each blot was obtained from samples run on parallel gels. For B, C, and E–H, data represent the mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01, by Student’s t test.