Figure 3. Duplications of enhancer elements result in Ihh over- and misexpression.
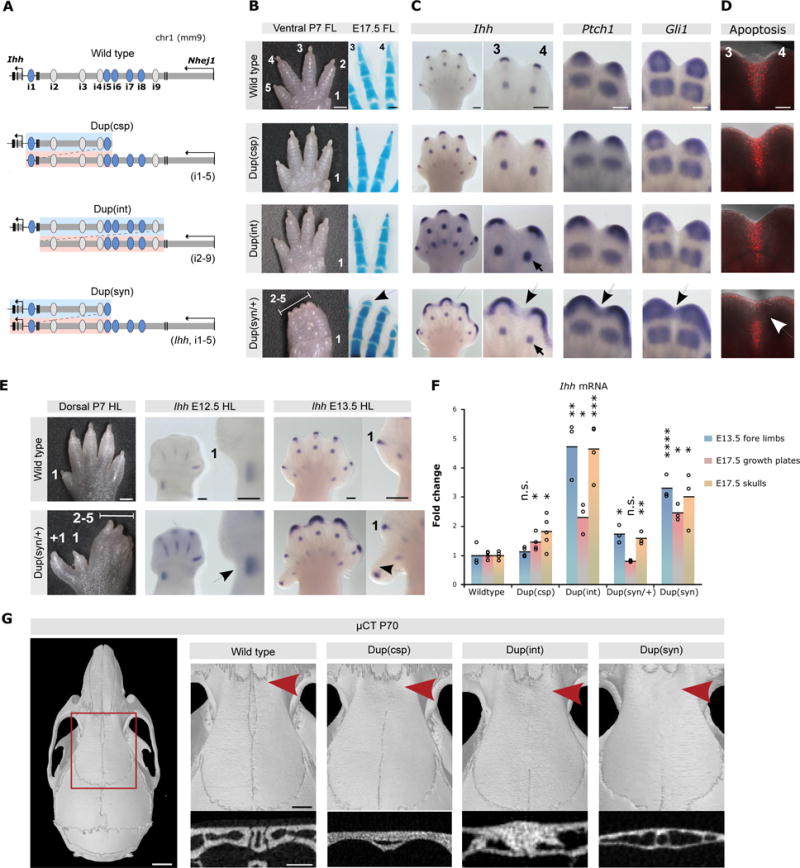
(A) Duplications generated by CRISVar21. Duplicated fragment shown in blue/pink. (B) Forelimb morphology (P7). Dup(int) and Dup(csp) mice (homozygous) are normal, but Dup(syn)/+ display 2/5 syndactyly. Skeletal stainings (right) show short and broad terminal phalanges in Dup(syn)/+ mice (arrow). Scale bars=1000μm (P7), 200μm (E17.5 handplates). (C) In situ hybridization shows increased and broadened expression of Ihh and downstream effectors Ptch1 and Gli1 [Dup(csp) < Dup(int) < Dup(syn)]. Expression domains in Dup(syn)/+ mice extend into distal interdigital space (arrows). Note increased Ihh expression in digit condensations in Dup(int) compared to Dup(syn)/+ (small arrow), also observed across entire handplate. Scale bars=200μm. (D) Apoptosis in interdigital space (red signal). Note lack of signal in distal region in Dup(syn)/+ mutants (arrow). Scale bars=200μm. (E) Hindlimb morphology of Dup(syn)/+ mice. Note preaxial polydactyly and syndactyly 2/5. In situ hybridization shows increased Ihh expression (arrows) in preaxial region (insets). Scale bars=1000μm (P7), 200μm (E12.5/E13.5). (F) Ihh qPCR analysis. Duplications increase Ihh expression. High levels in Dup(csp) forelimbs (no phenotype) result from digit condensations, while moderate upregulation in Dup(syn)/+ (syndactyly) derives from fingertips. Bars represent mean of n ≥ 3 different individuals (circles). *P< 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ns, not significant. (G) μCT skull analysis (P70). Red square indicates enlargement of metopic suture region (right). Below, cross section of metopic sutures (red arrow). All mutants display complete suture fusion [maximum effect in Dup(int)]. Scale bars=2mm (skull), 1mm (enlargement), 0.5μm (cross section).
