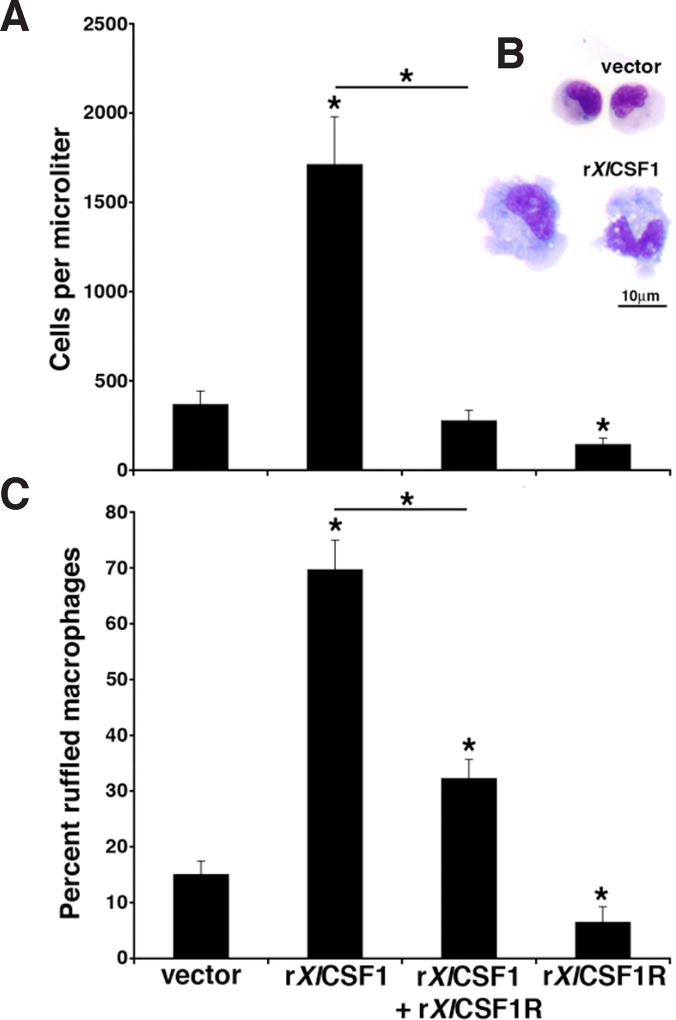
Fig. 6. The rXlCSF1R abrogates the rXlCSF1-mediated tadpole macrophage recruitment and differentiation.
(A) Tadpoles were injected with vector control, 250ng of rXlCSF1, 1000ng of rXlCSF1R or a combination of rXlCSF1 (250ng) and rXlCSF1R (10000ng). After 24hrs peritoneal phagocytes were lavaged and enumerated. Results are means ± SEM, N=6 and the (*) above lines denotes significant difference between treatment groups indicated by the lines, P<0.05. (B) Morphological analysis of Giemsa-stained vector-control and rXlCSF1R derived cultures. Scale bar = 10µm. (C) Cultures from (A) were Giemsa-stained, enumerated for the presence of morphologically differentiated macrophages as exemplified in (B) by the rXlCSF1R-derived cells. Results are expressed as percent means ± SEM from ten random fields of view. The (*) above lines denotes significant difference between treatment groups indicated by the lines, P<0.05.