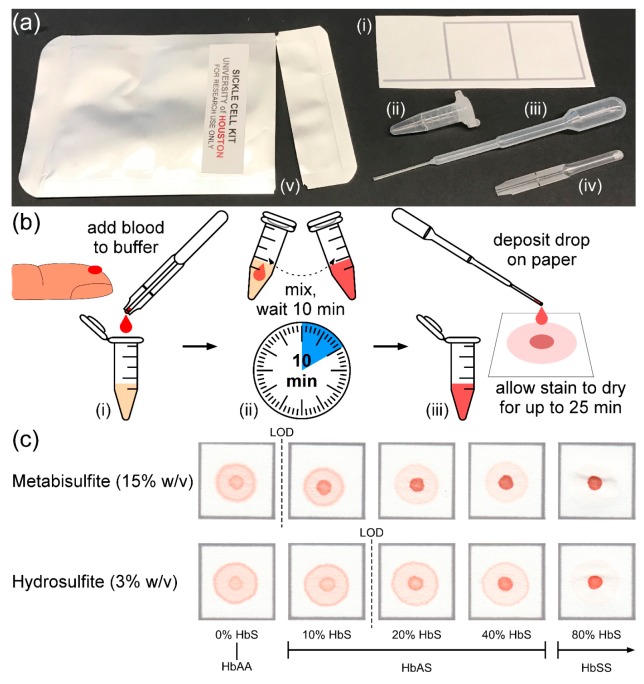
Figure 1.
Overview of the distributable paper-based SCA diagnostic test kit. (a) Photograph of the sickle cell kit with all components necessary to perform the test: (i) patterned chromatography paper; (ii) reagent tube containing reagents; (iii) reagent dropper; (iv) blood dropper; and (v) foil pouch. (b) Schematic illustration showing the steps required to perform the paper-based test: (i) ~20 μL of whole blood is collected via finger-stick using the blood dropper and deposited in the reagent tube; (ii) the blood is mixed with a preset volume of buffer (containing either sodium hydrosulfite or sodium metabisulfite) via manual agitation; and (iii) after 10 min, a drop (~20 μL) of the mixture is deposited on the chromatography paper using the reagent dropper and allowed to dry for up to 25 min before being evaluated visually. (c) Representative bloodstains produced by the metabisulfite (top) and hydrosulfite (bottom) versions of the paper-based test for samples with various sickle hemoglobin (HbS) concentrations. The limit of detection (LOD) for each version is indicated by a dashed line. Typical HbS concentration ranges for adults and children older than six months of age with different genotypes (normal—HbAA; SCT—HbAS; SCA—HbSS) are marked below the stains.