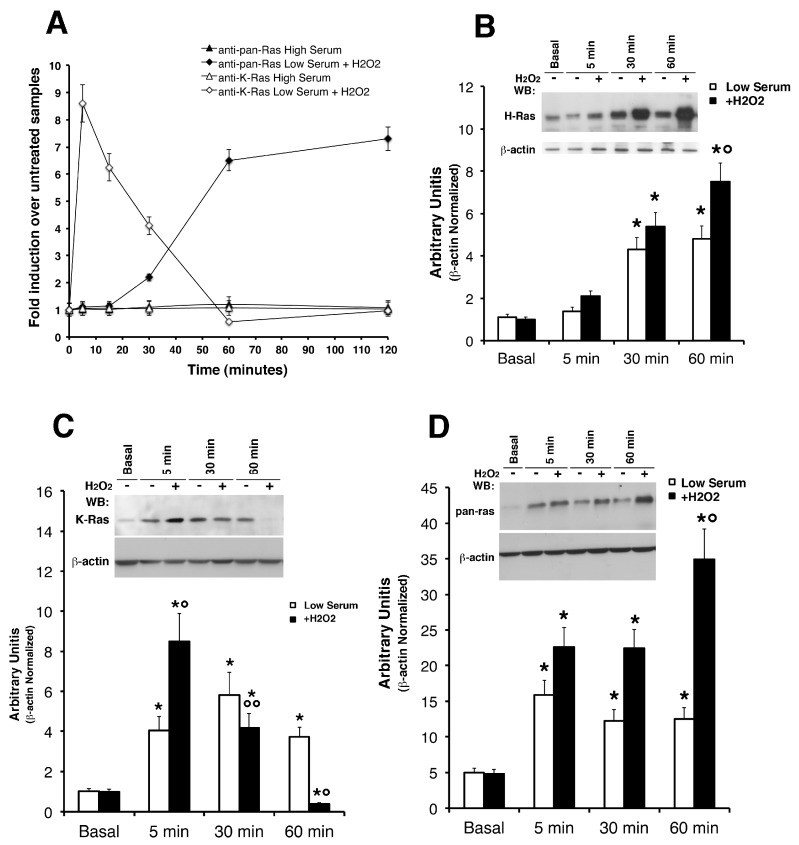
Figure 1.
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) selectively induce K-Ras and H-Ras protein levels in primary astrocytes. The direct effects of hydrogen peroxide addition in regulating the protein levels of K-Ras and H-Ras in cultured astrocytes were measured by western blot analysis. The kinetics of total p21Ras expression and K-Ras isoform in cultured astrocytes subjected to H2O2 treatment is shown in (Panel A). The growth medium (high-serum 20%) was switched into a low-serum (2%) medium containing or not H2O2 and western blot analyses were performed on Radioimmunoprecipitation (RIPA) buffer extracts. Total p21Ras protein shows constitutive low levels in untreated astrocytes and increases upon oxidative stimulation (Panel D). K-Ras (sc-521) levels increased in 5 min and rapidly decreased, reaching the basal levels at 60 min of stimulation (Panel C). Conversely, H-Ras protein levels peaked at 60 min and remained high for up to 120 min (Panel B); representative immunoblots with antibodies against H-Ras (sc-520) and pan-Ras (H259) show the same immune-reactivity pattern with differences in sensitivity. Monoclonal anti-β actin was used as loading control. Experiments were carried out in triplicates and statistical significance obtained by Student’s t-test. * p < 0.01 as compared with the untreated normal astrocytes (Student’s unpaired test); ° p < 0.02 as compared with the untreated sample (Student’s matched pairs test).