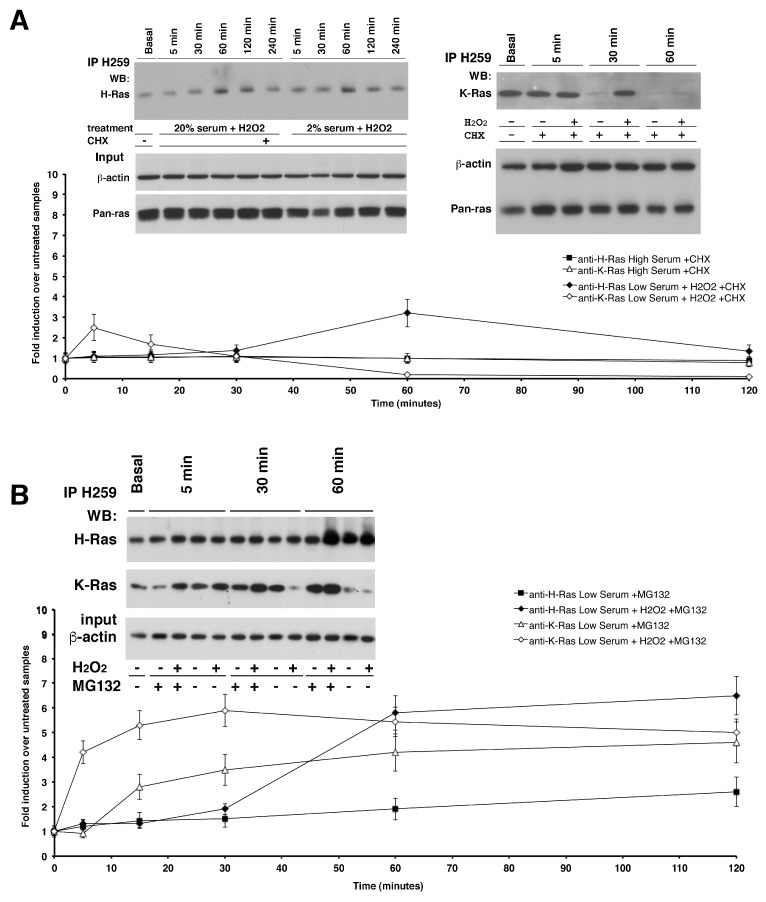
Figure 2.
Post-transcriptional regulation of K-Ras and H-Ras proteins by H2O2-induced oxidative stress. Western Blot analysis was performed on Y13-259 from astrocytes RIPA extracts that were cycloheximide (CHX) pre-treated or proteasomal inhibitor MG132 pre-treated and quickly subjected to H2O2 exogenous administration in complete medium or low-serum medium. In (Panel A), cultured astrocytes were pre-treated with the drug (CHX, 20 µg/mL) and the decay of the target protein over time was determined by western blot analysis with specific antibodies against H-Ras and K-Ras (left and right panel A, respectively). The addition of H2O2 shortened the expression of H-Ras (t1/2 values 1 h); conversely, H2O2 was able to induce K-Ras protein levels even in the absence of mRNA translation. Western blot analysis of total Ras (pan-Ras Ab-3) and monoclonal β-actin was performed in the same experiment and used as loading control (bottom panel). (Panel B) shows immunoblot analysis of H- and K- isoforms from immunoprecipitates of astrocytes pre-treated with the proteasome inhibitor, MG132, in the presence or absence of H2O2. Proteasomal inhibition prevented the reduction of K-Ras at 30 min, which maintained at high levels for up to 60 min. K-Ras protein also increased in cells treated with MG132, without H2O2, with kinetics mirroring mRNA accumulation. Total kinetics of K- and H- protein levels are shown in the bottom graph. All data derive from three independent experiments performed in triplicate (mean ± SD; n = 9).