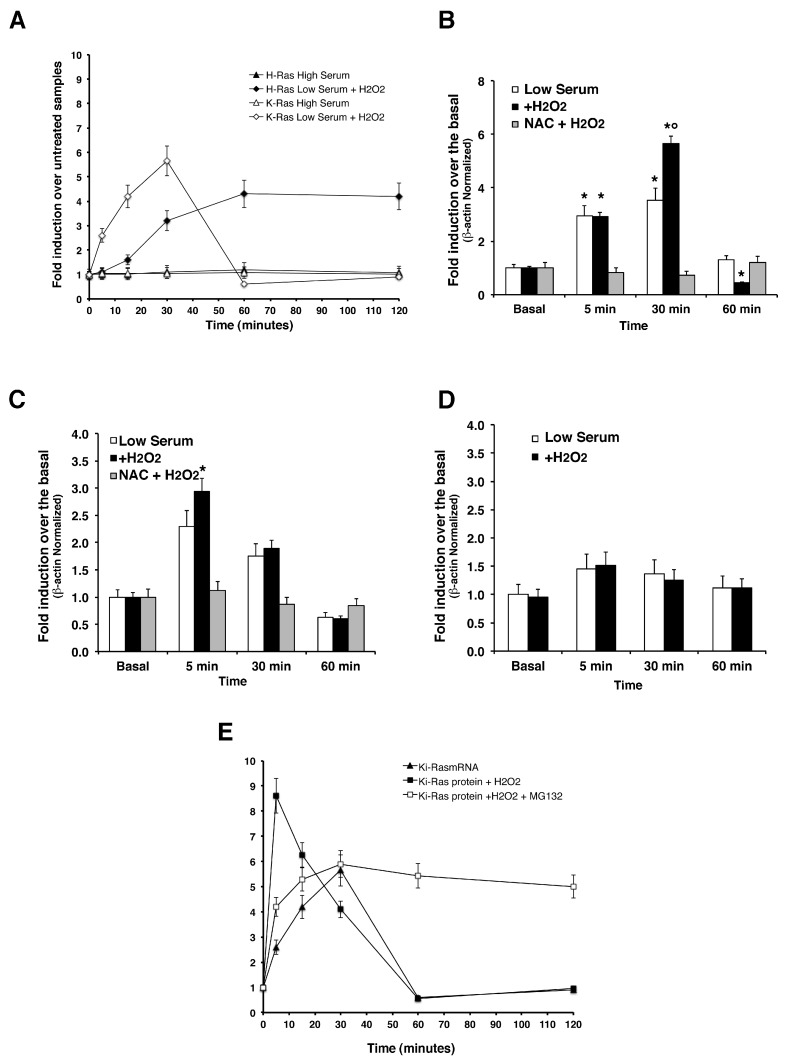
Figure 3.
Proto-oncogene K-Ras is transcriptionally induced by H2O2-induced oxidative stress in primary astrocytes. Quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) analysis of KRAS, HRAS, and iNOS in cultured astrocytes subjected to H2O2-induced oxidative stress or untreated (low-serum lacking H2O2 exogenous administration). The Panel A graph summarizes differences in total kinetics of K-Ras and H-Ras mRNA induction by H2O2 treatment in cultured astrocytes. Panel B, C, and D show mRNA fold induction of K-Ras, iNOS, and H-Ras, respectively, in primary astrocytes in presence or absence of N-Acetyl-cysteine (NAC) and in presence or absence of H2O2. To examine whether Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) formation was causally related to the mRNA increase, cultures were pre-treated with 5 mM N-acetylcysteine for 5 h prior to the medium switch. This pre-treatment dampened the mRNA induction in both conditions. Panel E summarizes translational and transcriptional K-Ras kinetics in astrocytes exposed to ROS. All experiments were carried out in triplicates and statistical significance obtained by one-way ANOVA analysis with Dunn’s post hoc * p < 0.01 and ° p < 0.05.