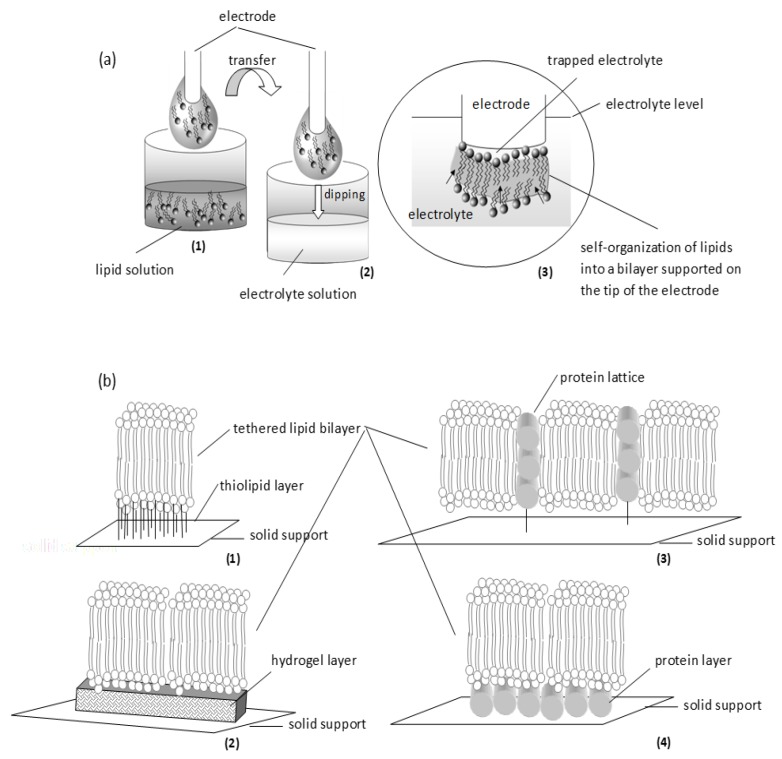
Figure 4.
Schematic of two simple approaches in supporting the bilayer: self-assembly (a) and tethering (b). (a) Self-assembly: (1) A metal wire (freshly cut) is dipped into lipid solution; when withdrawn, a small drop of lipid solution is attached around the tip. (2) The electrode is immersed in electrolyte solution. (3) On dipping into the aqueous phase, lipids gather spontaneously at the tip of the electrode (pushing along electrolyte molecules) to form a monolayer that drives other lipid molecules to cover it at the top; the assembly is finally thinned to a bilayer. (b) Tethering: Thiolipids (1) or hydrogels (2) can be used as the anchoring layer. Alternatively, proteins can be used either as a lattice (3) or as a layer (4).