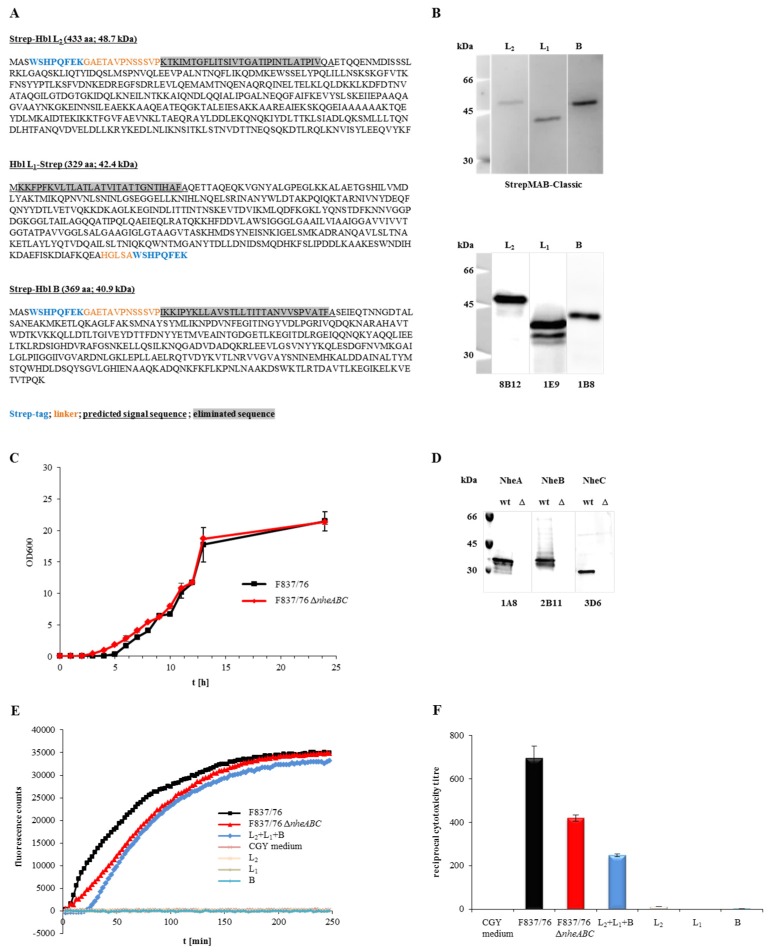
Figure 1.
Properties of the recombinant Hbl components and the nheABC deletion strain. (A) Amino acid sequences of rHbl L2, L1 and B. Strep-tags are shown in blue, linker amino acids in orange letters, the predicted secretion signal sequences are underlined and eliminated sequences are highlighted in grey. From these sequences the molecular weight was predicted (http://web.expasy.org/compute_pi/). (B) Detection of the rHbl components in Western blots. The strep-specific StrepMAB-Classic was used for detection (upper blot), as well as the Hbl-specific mAbs 8B12 (L2) [32], 1E9 (L1) [29] and 1B8 [29] (lower blot). (C) Growth of B. cereus strains F837/76 and F837/76 ∆nheABC in LB medium. Medium was inoculated to an OD600 of 0.005 and growth at 37 °C was monitored for 24 h. (D) Western blot. NheA, B and C were detected in the supernatant of strain F837/76 using the mAbs 1A8 [20], 2B11 [20] and 3D6 [21], respectively. These proteins were not detected in the supernatant of the nheABC deletion mutant. (E) Influx of PI into Vero cells, represented by increasing fluorescence counts. 1.5 pmol/μL rHbl components were either used separately or mixed in a 1:1:1 ratio and applied in 1:40 dilution to the cells, as was supernatant of F837/76 ∆nheABC. CGY medium and supernatant of F837/76 were used as controls. (F) Results of a WST-1-bioassay (Vero cells) determining toxic activity of the nheABC deletion strain and the rHbl components (1.5 pmol/μL each, separately or mixed in a 1:1:1 ratio). CGY medium and supernatant of F837/76 were used as controls.