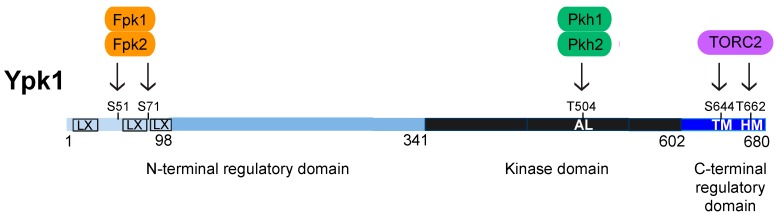
Figure 1.
Schematic depiction of the primary structure of Ypk1. Catalytic domain (black) and N- (light blue) and C-terminal (dark blue) regulatory elements are indicated. Shading reflects percent sequence identity between Ypk1 (680 residues) and the corresponding segment in its paralog Ypk2 (677 residues): 1–98, 22% (faint blue); 99–341, 62% (medium blue); 342–602, 90% (black); and, 603–680, 73% (dark blue). Abbreviations: LX, low-complexity sequences predicted by UnitProt [50] and/or SMART [51] databases; AL, activation loop Thr (T504), phosphorylated by Pkh1 and, less efficiently, by Pkh2 [46]; TM, turn motif Ser (S644), phosphorylated by TORC2; and, HM, hydrophobic motif Thr (T662), phosphorylated by TORC2. Two N-terminal residues phosphorylated by Fpk1 and, less efficiently, by Fpk2 [52] are also shown.