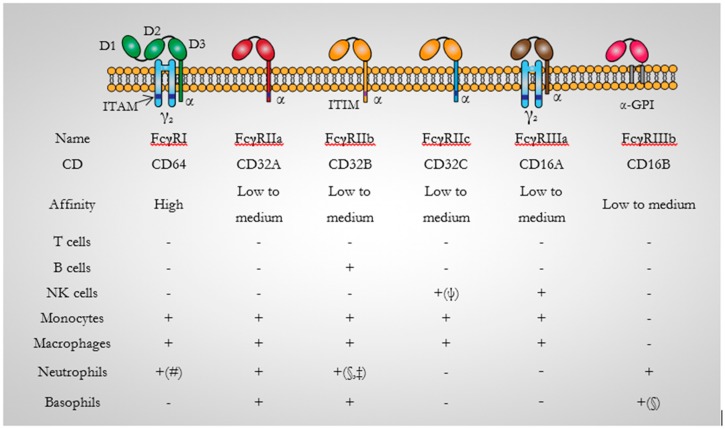
Figure 2.
Diagrammatic representation of the human Fc receptors. There are five activating FcγRs: FcγRI, FcγRIIa, FcγRIIc, FcγRIIIa, FcγRIIIb, and one inhibitory Fc receptor; FcγRIIb. They all consist of an immunoglobulin-binding polypeptide chain with two Ig-like extracellular domains with the exception of FcγRI (CD64) which has three. An activating signalling cascade is mostly generated by the cross-linking of activating FcγRs by immune complexes which results in the phosphorylation of ITAMs on FcγRIIa and FcγRIIc. The FcR-γchain common to the Fc receptors is the only inhibitory FcγR. FcγRIIb also binds immune-complexed IgG and contain an ITIM in its cytoplasmic domain. ITAM: immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif; γ2: dimer of FcRγ subunits; ITIM: immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motif; GPI: glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol; NK cells: Natural Killer cells; +: indicates expression; (-): No expression; (#): only on activated Neutrophils; (§): Low; (‡): conflicting reports: (ψ): expressed only in 30% of humans [32,36].