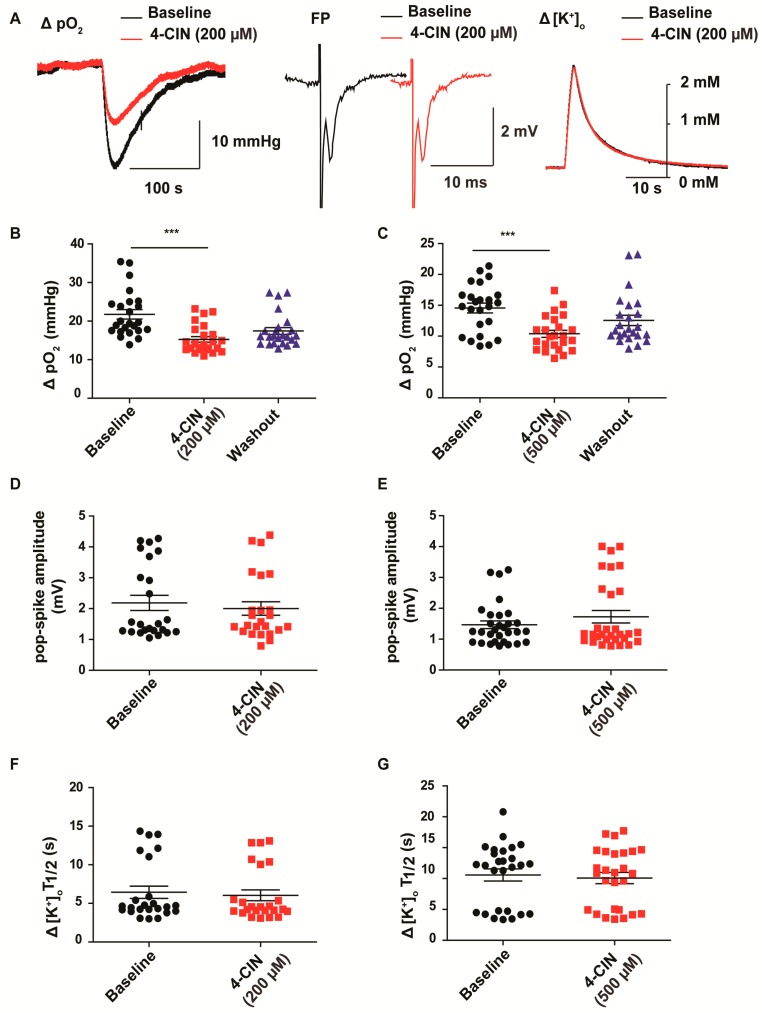
Figure 1.
Effects of monocarboxylate transporter (MCT) inhibition by α-cyano-4-hydroxycinnamic acid (4-CIN) on stimulus induced extracellular tissue oxygen changes (ΔpO2), field potential responses (FP), amplitude and recovery kinetics of extracellular K+ concentration changes (Δ[K+]O). Despite the clear effect on the stimulus induced pO2 changes neither recovery kinetics of Δ[K+]O nor field potential amplitude were affected by 4-CIN. (A) Sample traces of ΔpO2 (left), field potential transients (middle) and Δ[K+]O (right) in the presence and the absence of 4-CIN. Inhibition of the MCTs decreased ΔpO2 both at (B) 200 µM and (C) 500 µM 4-CIN concentration, (D,E) whereas it did not affect field potential amplitude and (F,G) first half recovery time of Δ[K+]O for both concentrations, respectively; (B–G) Variables are given on the Y-axis, categories of treatment on the X-axis. *** p < 0.001.