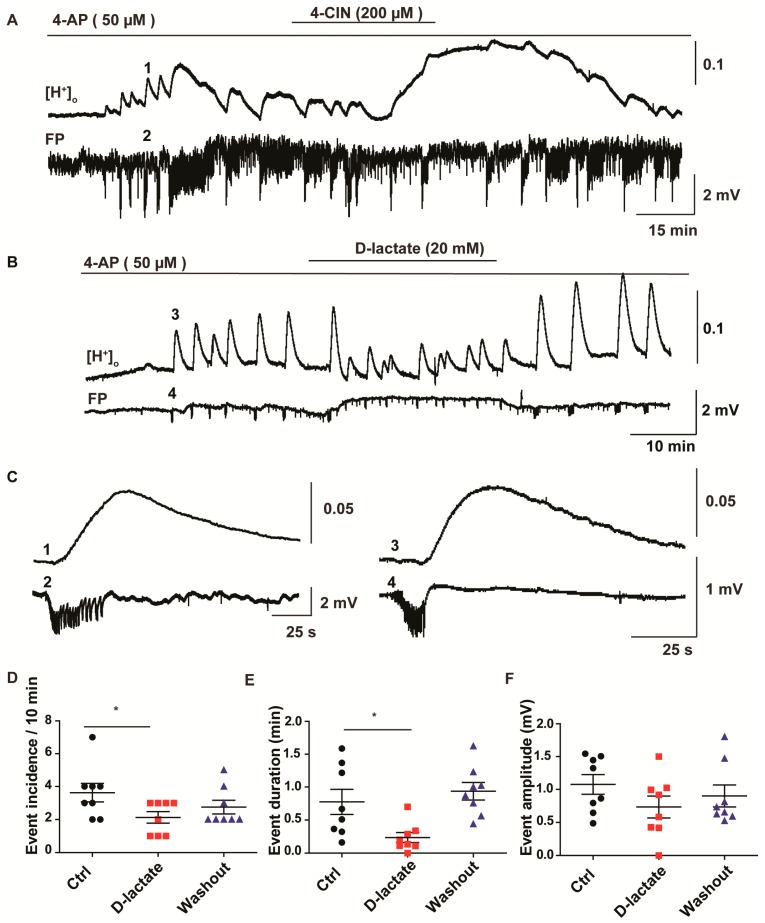
Figure 4.
Effect of MCT inhibitors—4-CIN and d-lactate—on baseline and SLE-associated changes in extracellular pH. Extracellular H+ ion concentration was measured using ion sensitive electrodes; hence the displayed traces show change in H+ ion concentration which got converted to pH units. (A) Application of 4-CIN resulted in a late onset baseline acidotic shift; (B) In contrast, application of sodium d-lactate (20 mM, osmolality and pH set as in normal aCSF) did not induce changes in baseline pH while exerting similar inhibitory effects on 4-AP induced epileptic form activity; (C) Sample trace of single SLE with corresponding pH change in different time scale. Each individual SLE was associated with small acidotic shifts in both 4-CIN (1,2) and d-lactate (3,4) experiments, traces taken from the recordings in (A,B) as shown by the corresponding number; (D) SLE incidence and (E) duration (F) but not the amplitude were significantly decreased; (D–F) Variables are given on the Y-axis, categories of treatment on the X-axis. * p < 0.05. Each dot represents a single data point, black dots represent 50 µM 4-aminopyridine (4-AP) application, red dots represent 20 mM d-lactate and 50 µM 4-AP application, blue dots represent washout in 50 µM 4-AP.