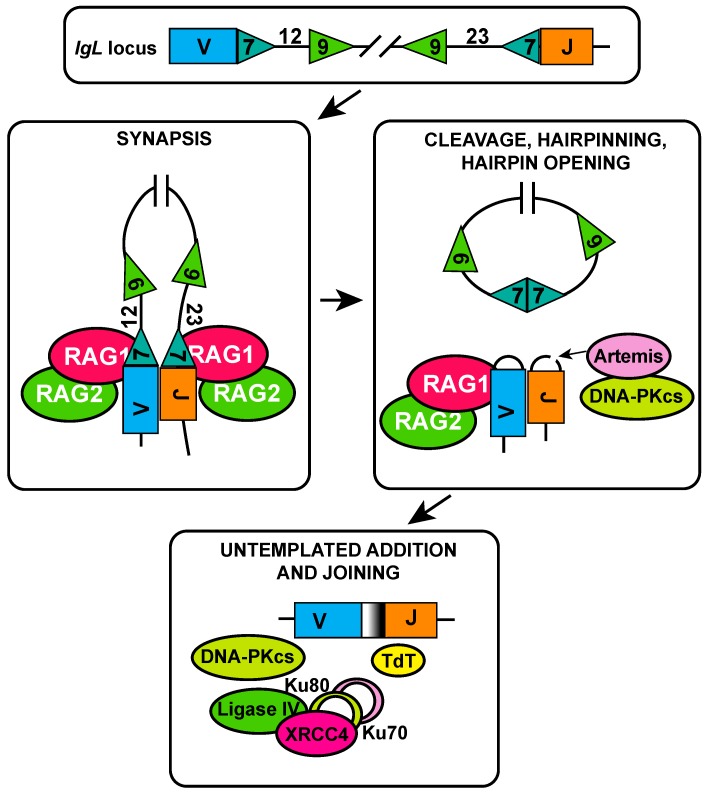
Figure 2.
Molecular mechanism of V(D)J recombination. Schematic representation of immunoglobulin light chain loci (IgL) showing a V gene segment flanked by 12-base pair (bp) spacer recombination signal sequence (RSS) and a J gene segments flanked by a 23-bp spacer RSS. The recombination activating gene 1/2 complex (RAG1/2) forms a synaptic complex with a 12-bp spacer RSS and a 23-bp spacer RSS, resulting in nicking and hairpin formation at the coding ends. RSS heptamers are joined to form a signal joint. Artemis is required for coding end hairpin opening and is activated by the DNA protein kinase catalytic subunit (DNA-PKcs). Upon hairpin opening, terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (TdT) adds untemplated nucleotides and increases junctional diversity. Ends are sealed by non-homologous end joining (NHEJ), requiring Ku70 (depicted in pink), Ku80 (depicted in light green), XRCC4, DNA ligase IV, and DNA-PKcs.