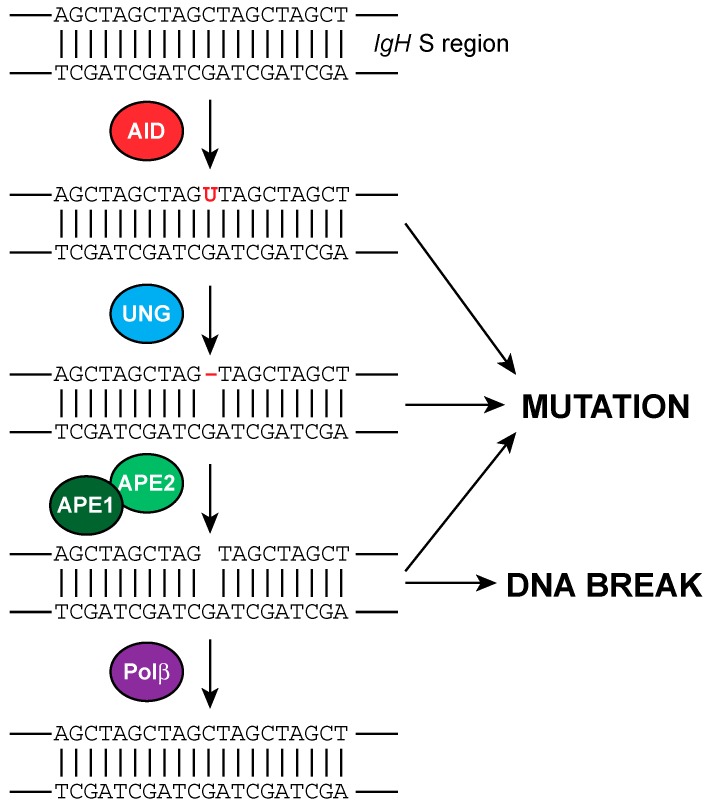
Figure 5.
Involvement of BER proteins in CSR. During immunoglobulin (Ig) class switch recombination (CSR) activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID) converts cytosines into uracils (shown in red font color) in the Ig heavy chain (IgH) switch (S) regions. Processing of the resulting uracils lead to either DNA mutations or DNA breaks, or can be faithfully corrected. AID-instigated uracils are processed by the base excision repair (BER) pathway. Replication across a uracil can lead to C-to-T/G-to-A transition mutations. Alternatively, the uracil is removed by uracil-DNA-glycosylase (UNG) leading to an apyrimidinic/apurinic (AP) site (shown as red dash), which, when replicated, result in either transition or transversion mutations. The AP site can also be cleaved by AP endonuclease 1 and 2 (APE1/2), which when sufficiently close on either strand results in the formation of a DNA break, or when spaced further apart require the mismatch repair (MMR) pathway to be converted into DNA double-strand breaks. DNA polymerase β (Polβ) is required for faithful repair of the APE1/2 nicked DNA backbone, and would thereby diminish Ig CSR.