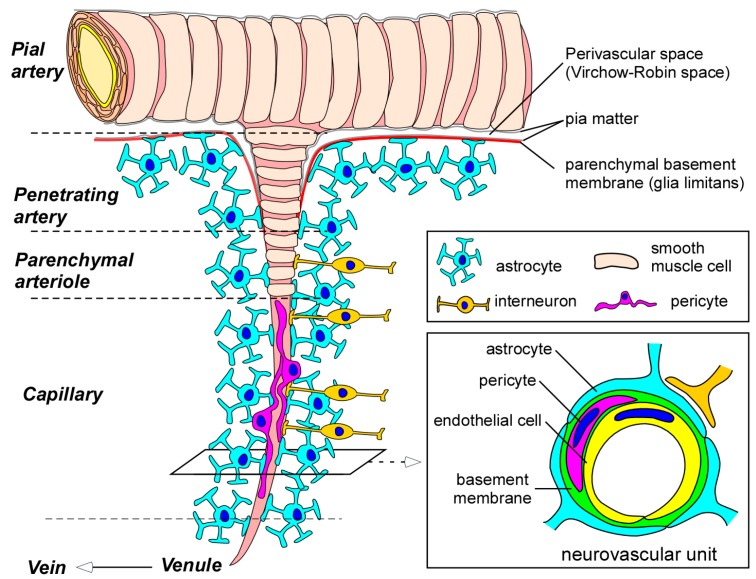
Figure 1.
Blood-brain barrier (BBB) and the neurovascular unit. Pial arteries branch out into smaller arteries called penetrating arteries. The penetrating arteries go further down into the brain parenchyma, giving rise to parenchymal arterioles, which eventually branch off into capillaries. Whereas pial and penetrating arteries are covered by vascular smooth muscle cells and are separated from brain tissues by the parenchymal basement membrane (glia limitans), parenchymal arterioles and capillaries become associated with neurons and astrocytes. Parenchymal arterioles are covered by one layer of smooth muscle cells. In capillaries, endothelial cells form the BBB. BBB properties in endothelial cells are further maintained and regulated through communications with basement membranes and other neighboring cells in neurovascular unit such as pericytes, astrocytes, and interneurons. BBB indicates blood-brain barrier.