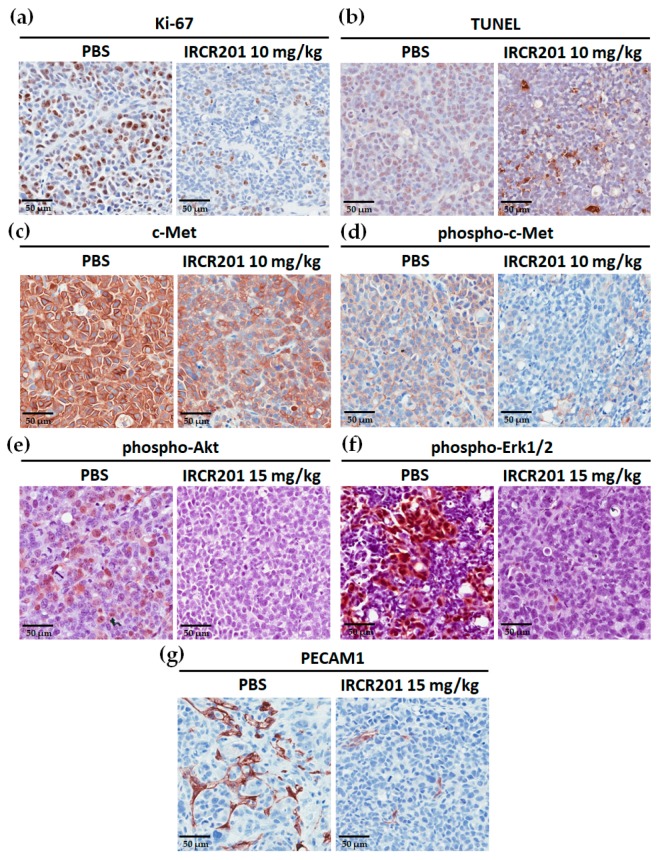
Figure 9.
Immunohistological staining of Ki-67, apoptotic cells, c-Met, phospho-c-Met, phospho-Akt, phospho-Erk1/2, and platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule 1 (PECAM1) in an MKN45 xenograft mouse tumor model. (a–g) All the immunohistochemistry (IHC) images were obtained at the same magnification. Sections were counterstained with hematoxylin (blue); (a–d) Immunohistochemistry analysis of MKN45 tumors in mice at 48 h post-treatment with 10 mg/kg IRCR201. The control group was intravenously injected with PBS (vehicle); (a) Immunohistological staining of MKN45 tumor section for Ki-67 (brown); (b) Immunohistochemistry analysis of apoptotic cells (brown) using the terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling (TUNEL) assay; (c,d) IHC expression images of total c-Met (brown) and phospho-c-Met (brown) in the MKN45 tumor section at 48-h post-treatment at 10 mg/kg; (e–g) Immunohistochemistry analysis of phospho-Akt, phospho-Erk1/2, and PECAM1 on 15 mg/kg IRCR201-treated MKN45 tissue sections; (e,f) IHC expression images of phospho-Akt (brown) and phospho-Erk1/2 (brown) in the MKN45 tumor sections; (g) Immunohistological analysis of PECAM1-positive blood vessels (brown) in the 15 mg/kg IRCR201-treated MKN45 xenograft tumor section.