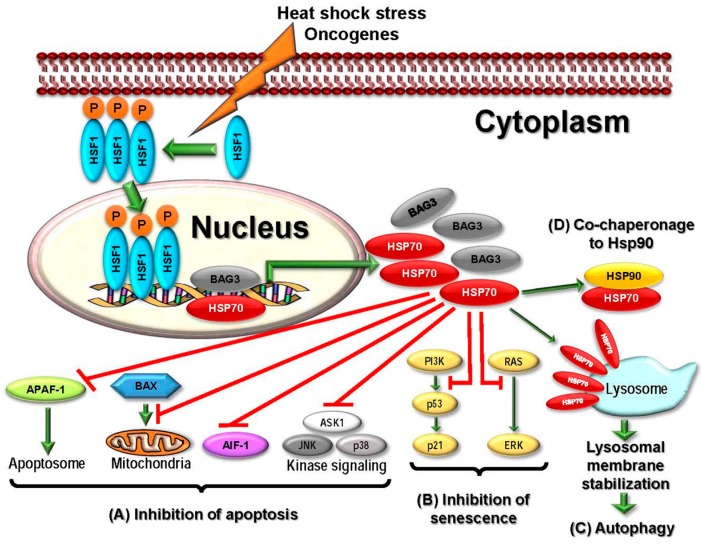
Figure 6.
Diverse roles of HSP70 in carcinogenesis in response to stress. Activation of HSF1 in response to heat shock stress and oncogenic activation (orange lightning) leads to overexpression of HSP70 and its co-chaperones (e.g., Bag3) promoting tumorigenesis through the following mechanisms: (A) Suppression of apoptosis: Hsp70 inhibits both intrinsic and extrinsic apoptotic pathways by blocking APAF1 recruitment to apoptosome, inhibiting BAX translocation to mitochondria, suppressing AIF-1 expression and other stress-induced kinases; (B) Bypass of senescence: HSP70 inhibits both p53-dependent and-independent senescence pathways; (C) Promotion of autophagy: Localization of HSP70 to the lysosomes in cancer cells stabilizes the lysosomal membrane to promote autophagy, and (D) Activation of additional HSPs: HSP70 serves as a co-chaperone to HSP90 and is required for the proper maturation of HSP90 client proteins such as HER2, AKT, and CRAF.