Figure 5.
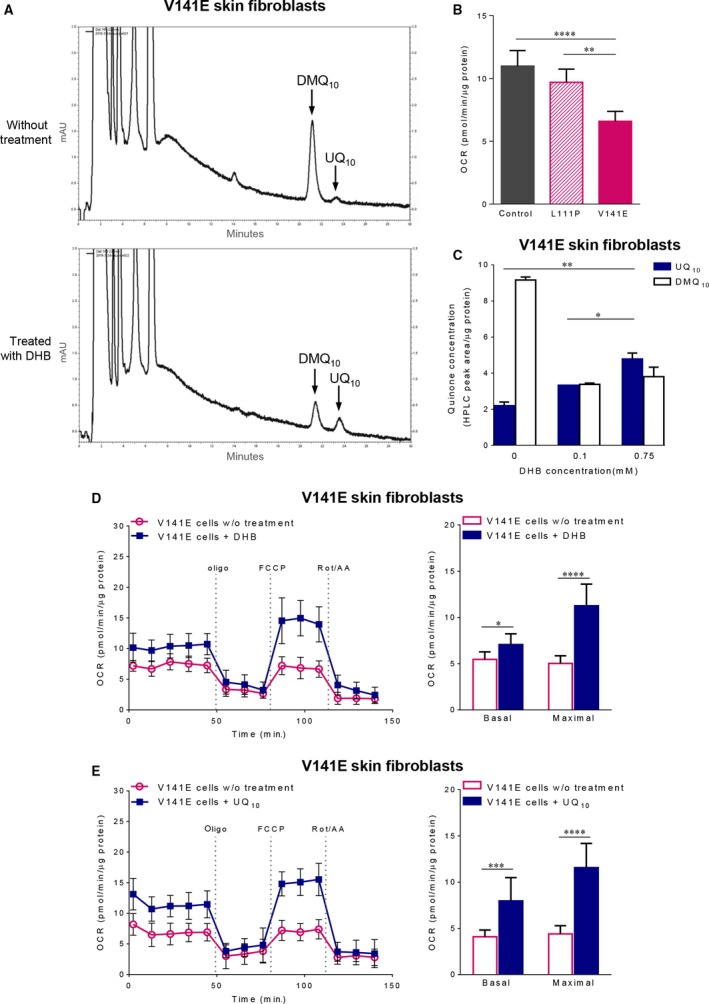
The effects of DHB on the skin fibroblasts derived from the V141E COQ7 patient. (A) HPLC chromatograms of quinone extracts from V141E skin fibroblasts. The patient cells showed a substantial reduction in UQ10 levels and a large accumulation of DMQ10. After treatment with 0.75 mM DHB, there was a significant increase in UQ10 levels, which was accompanied with a lesser accumulation of DMQ10. Cells with the same amount of protein (2.1 mg) were used for quinone extraction and HPLC quantitation. (B) Basal mitochondrial respiration rates measured using a Seahorse XF24 Analyzer. Data were collected from five cultures in each group and are expressed as means ± S.D. **P < 0.01, ****P < 0.0001 (one‐way anova followed by Tukey's multiple comparison test). (C) DHB increases UQ10 production and decreases DMQ10 accumulation in the V141E patient cells. Quinone levels are expressed as HPLC‐UV peak area normalized to protein content, and shown as mean ± S.E.M. (n = 2). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 (one‐way anova followed by Tukey's multiple comparison test). (D) The effect of DHB treatment on mitochondrial respiration in V141E skin fibroblasts. (E) The effect of UQ10 on mitochondrial respiration in V141E skin fibroblasts. The experimental condition and data acquisition in D and E are the same as in Figure 4. Shown on the left are representative OCR traces. Quantitative data are graphed on the right as mean ± S.D. (n = 9–10/group). *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001 by two‐way anova with Sidak's multiple comparison test.
