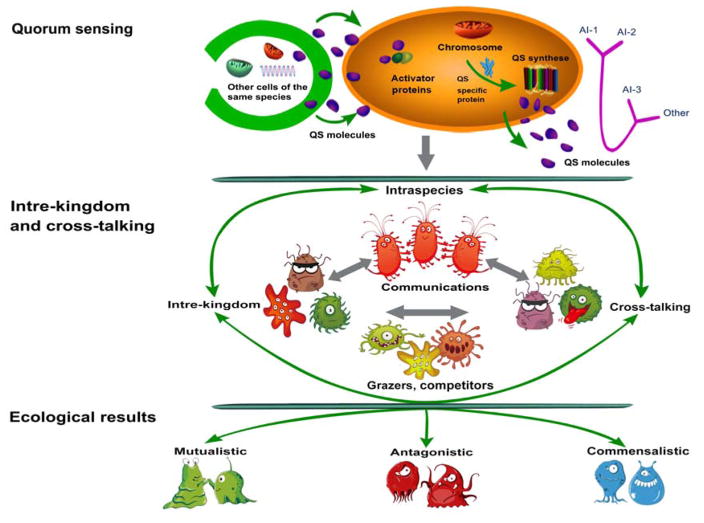
Figure 3.
Formation and multifunctional roles of QS in algal-bacterial symbiosis. Top: quorum sensing (QS) molecules are produced in the bacterium by QS synthesis and diffuse from the cell to enter neighboring bacteria. QS signaling molecules bind to the receptor polypeptide, leading to formation of active dimers. The receptor dimers bind to specific promoter sequences in the bacterial genome and activate the transcription of certain sets of genes. Middle: microbial communication by QS molecules, including intre-kingdom and intra-species communication, interspecies cross-talking, and other communication among different species. Bottom: QS-mediated social cooperation and conflict in algal-bacterial symbionts, such as mutualistic, antagonistic, and commensalistic symbionts.