TABLE 1.
QS signals and their characterization in marine microorganisms
| QS signal | Producing species | Chemical structure | Physical properties | Molecular synthase | Regulated protein | Ecological function | References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AI-1 short-chain molecules |
C4-HSL | Vibrio harveyi | Homoserine lactone (HSL) ring with a variable acyl side chain.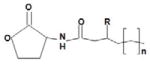
|
Molecular weight: from 171.9 Da for a C4- to 367.57 Da for an unsubstituted C 18-AHL (Decho et al., 2011). Solubility: low-molecular-weight AHLs tend to be relatively water soluble, and it is unlikely that communal responses based on their presence would ever be limited by their solubility. However, as molecular weights increase significantly above 520 g/mol, the saturation concentration of the AHL is expected to drop below 1μM AHL (Decho et al., 2011). Diffusivity: from 10 to 78 μm AHL (Decho et al., 2011). Dispersion: from 10 s micrometers to 100 s micrometers AHL (Decho et al., 2011). |
LuX-M | LuxR type protein | Bioluminescence | Waters and Bassler (2005) |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa | RH II | Biofilm maturation | Waters and Bassler (2005) | |||||
| Aeromonas hydrophyla |
Ahy I
Asa I |
Biofilm formation, Enzyme production | Tebben et al. (2011) | |||||
| Serratia marcescens | SWrI | Swarming | Miller and Bassler (2001) | |||||
| C6-HSL | Erwinia stewartii G− | LuXI | LuxR type protein | Exopolysaccharide | Watson et al. (2002) | |||
| Vibrio fischeri G− | Light production | Nealson et al. (1970) | ||||||
| P. fischeri G− | Virulence | Eberhard et al. (1981) | ||||||
| A. salmonicida | Ahy I | LuxRtype protein | Biofilm formation | Swift et al. (1999) | ||||
| Chromobacterium Violaceum | CV I | Violacein, antibiotics, and enzyme production | Cha et al. (1998) | |||||
| Yersinia enterolcolitica, Y. pseudotuberculosis | Yen I, Yps I | Motility aggregation | Miller and Bassler (2001) | |||||
| Vibrio sp. (algae-associated) | LuxI | Settlement activity | Taylor et al. (2007) | |||||
| Vibrio alginolyticus | LuxI | / | Huang et al. (2007) | |||||
| C8-HSL | Agrobacterium tumefaciens | Tra I | Virulence factors | Fuqua et al. (2001) | ||||
| Y. pseudotuberculosis | Yps I | Potential regulate cells wimming | Miller and Bassler (2001) | |||||
| Roseobacter spp., Marinobacter sp. | / | / | Taylor et al. (2007) | |||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| AI-1 long-chain molecules |
C10-HSL | Vibrio anguillarum | Van I | LuxR | Virulence | Defoirdt et al. (2004) | ||
| C12-HSL | Vibrio alginolyticus | Las I | LuxR | Virulence formation | Pearson et al. (1994) | |||
| / | LuxR | / | Huang et al. (2007) | |||||
| C14-HSL | Roseobacter sp. | / | LuxR | / | Mohamed et al. (2008) | |||
|
| ||||||||
| AI-2 | Furanosyl borate diester | Vibrio harveyi | The proposed structure contains two fused five member rings containing one boron atom bridging the diester.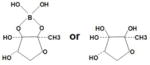
|
/ | Ai-2 | Bioluminescence | Bassler et al. (1993) | |
| V. cholerae | Ai-2 | Virulence | Chen et al. (2002) | |||||
| V. harveyi | Ai-2 | Virulence | Henke and Bassler (2004) | |||||
| 2-methy-2,3,3,4-tetrahydroxytetrahydrofuran | V. parahaemolyticus | Cqs A | Virulence | Miller et al. (2002) | ||||
| V. cholerae | Ai -2 | Virulence | Miller et al. (2004) | |||||
| Salmonella enterica | Virulence gene expression | Sperandio et al. (2001) | ||||||
| Escherichia coli | Type II secretion | Day and Maurelli (2001) | ||||||
| Shigella flexneri | LupX | Virulence factor virB expression | Mcnab et al. (2003) | |||||
| Streptococcus pordonii | Biofilm formation | Li et al. (2002) | ||||||
|
| ||||||||
| AI-3 | E. coli, Xanthomonas campestris | DSF:cis-11-methyl-2-dodecenoic acid. |
/ | LuxS | Lux P/Q type protein | Biofilm formation | Barber et al. (1997) | |
| Lux O type protein, mRNA-dependent regulation, such as 5RNAs | Reading and Sperandio (2006); Wang et al. (2004) | |||||||
|
| ||||||||
| Peptide autoinducers | Cyclic dipeptides |
Pseudomonas sp. Streptomyces griseus Staphylococcus aureus |
Diketopiperazines (DPKS)* cyclo (L-Ala-L-Val) and cyclo (L-Pro-L-Tyr).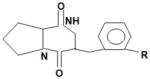
|
/ | LuxR | Activates AHL biosensors. *: the induction threshold for DKPS is higher than AI-1, which indicates that DKPS may not have a significant role in the marine environment |
Degrassi et al. (2002) | |
| Butyrolactonase | Waters and Bassler (2005) | |||||||
| Thiolactone | Lyon et al. (2000); Zhang and Dong (2004) | |||||||
|
| ||||||||
| Others | Bradyoxetin | Bradyrhizobium japonicum G−, Rhizobium sp., Alphaproteobacteria sp., Pseudomonas aeruginosa | 2-{4-[[4-(3-aminooxetan-2-yl)phenyl](amino)methyl]phenyl} oxetan-3-yl amine. |
/ | Nod gene | Nod gene | Nitrogen-fixing | Loh et al. (2002a,b) |
| Hydroxy palmitic acid methyl ester | Ralstonia solanacearum | PhcS-phcR | Iron concentration | Polysaccharide biosynthesis | Flavier et al. (1997) | |||
| Cys-11-methyl-2-dodecenoic acid | Xanthomonas campestris | / | Virulence | Zhang and Dong (2004) | ||||
| Non-identified compounds | Algae symbiotic bacterium | / | Competence, Morphogenesis | Decho et al. (2011) | ||||
