Figure 6. mTOR inhibitor protects B-ALL in vivo causing greater relapse after chemo.
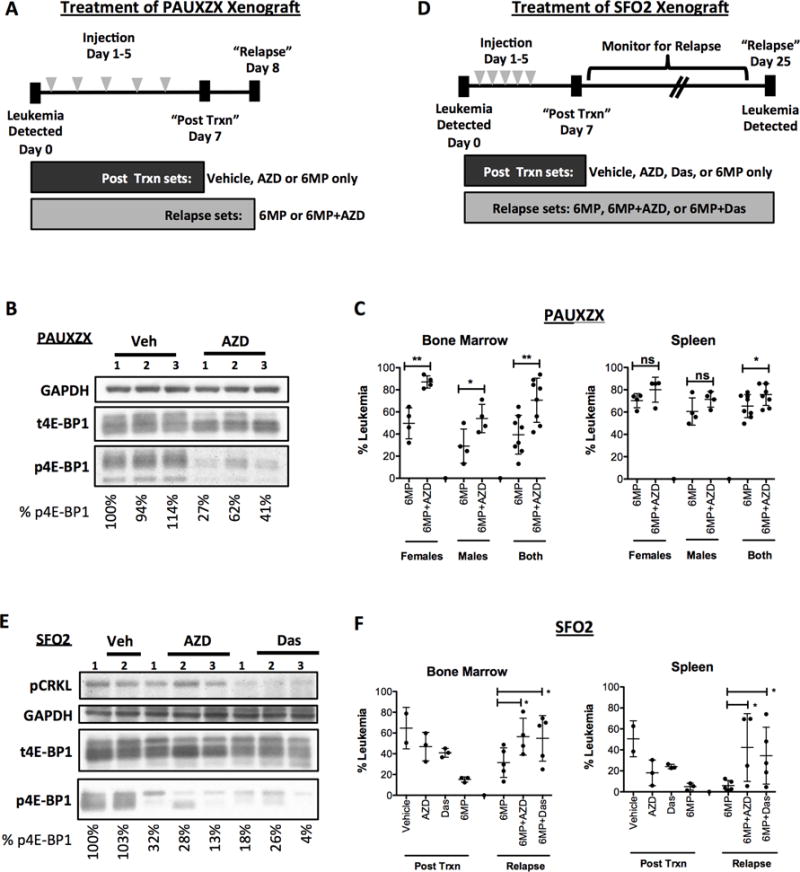
(A) For in vivo relapse assays, NSG mice were treated for 5 days (dosed once a day) upon detection of at least 1% PAUXZX leukemia in their peripheral blood. Control mice were treated with vehicle, AZD8055 or 6-MP only. Experimental mice were all dosed with 6-MP in addition to vehicle or AZD8055. The post treatment control mice were sacrificed 7 days after treatment was started. The experimental mice were sacrificed on day 8. (B) Control post-treatment mice were dosed with vehicle or AZD8055 2 hours before sacrifice on day 7. Spleen cells were harvested and Western blot analysis was done to determine effect of AZD8055 on mTORC1 activity as measured by p4E-BP1. (C) The leukemia burden in the bone marrow and spleen of the “relapse” PAUXZX sets were detected using human CD19 versus mouse CD45. (D) NSG mice were treated for 5 days (dosed once a day) upon detection of at least 1% SFO2 leukemia in their peripheral blood. Control mice were treated with vehicle, AZD8055, dasatinib or 6-MP as single agents. Experimental mice were all dosed with 6-MP in addition to vehicle, AZD8055 or dasatinib. The post treatment control mice were sacrificed 7 days after treatment was started. The experimental mice were monitored until relapse was detected in their peripheral blood, upon which time they were sacrificed (day 25). Note that during this period, one mouse in the 6MP+AZD set died, likely due to toxicity of the 6MP+AZD combination. (E) Control Ph+ SFO2 injected mice were treated with vehicle, AZD8055 alone or dasatinib alone. On day 7, mice were dosed with one final dose of inhibitor and sacrificed 2 hours after dosing. Western blot was performed on their bone marrow cells to detect inhibition of mTOR pathway by inhibitors. (F) The bone marrow and spleen of the control “post-treatment” and experimental “relapse” mice were obtained. The percentage of leukemia in bone or spleen were detected by staining human CD19 versus mouse CD45. Unpaired t-test was done for each comparison, mean±SD, *p<0.05, **p<0.005, ***p<0.0005.
