Figure 1.
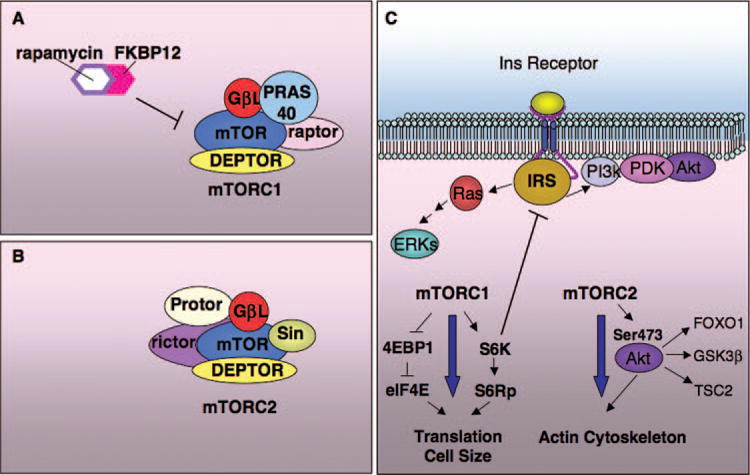
Schematic overview of the mTOR complexes, mTORC1 and mTORC2, and of the feedback loop. (A) The rapamycin-sensitive mTORC1 comprises, in addition to the mTOR kinase, raptor, GβL, PRAS40, and DEPTOR. (B) mTORC2 contains Rictor, GβL, Protor, Sin, and DEPTOR. (C) mTORC1 regulates translation, cell size, and the cell cycle, as well as autophagy and cellular metabolism. mTORC2 regulates the cellular cytoskeleton. In addition, mTORC2 is the kinase responsible for phosphorylation of Akt in Ser473. Activation of mTORC1 results in regulation of a negative feedback loop through which S6K inhibits the insulin receptor signaling by phosphorylating and inducing degradation of the adaptor IRS. As a consequence, activation of mTORC1 downregulates PI3k/Akt and the ERKs, whereas inhibition of mTORC1 upregulates both cascades.
