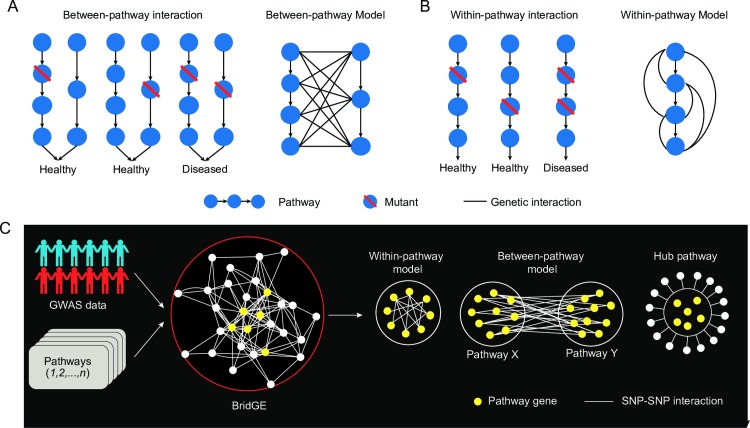
Fig 1. Pathway-level genetic interaction models.
(A) Between-pathway interaction and between-pathway model. Two biological pathways share a common function necessary for maintaining a healthy state. Genetic variants in individual pathways do not result in a phenotype, but joint mutations in both pathways in the same individual results in disease. Between-pathway interactions clustering between two complementary pathways and appear are referred to as an instance of the between-pathway model (BPM). (B) Within-pathway interaction and within-pathway model. A single pathway supports a function for maintaining a healthy state. A single genetic variant does not result in a phenotype, but joint mutations in the same pathway results in the loss of function and a disease state. Within-pathway interactions clustered within the single pathway are called a within-pathway model (WPM). (C) Overview of the framework for discovering pathway-level genetic interactions from GWAS breast cancer data, leveraging the BridGE method [23].