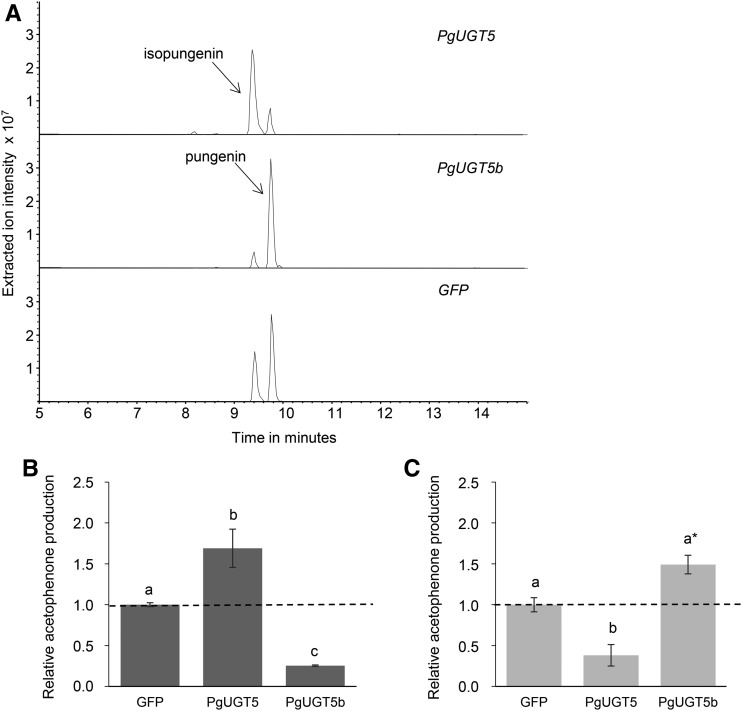
Figure 4.
Pungenol glycosylation activity in planta demonstrated that PgUGT5 and PgUGT5b function as pungenol glycosyltransferases when expressed in N. benthamiana. Leaves of 4-week-old N. benthamiana plants were transiently transformed for PgUGT5, PgUGT5b, or GFP (control) expression. Six days following the transformation, leaves were infiltrated with purified pungenol. Four hours after pungenol infiltration, metabolites were extracted and analyzed for acetophenones by LC-MS. A, Extracted ion chromatograms (−313) of glucosylated pungenol showed that plants transiently transformed for PgUGT5 expression accumulated higher levels of isopungenin, while plants transiently transformed for PgUGT5b expression accumulated higher levels pungenin, relative to the background profile of these metabolites in plants transiently transformed for GFP expression. B and C, Amounts of isopungenin and pungenin produced in plants transiently transformed for PgUGT5 or PgUGT5b expression relative to their amounts produced in plants transiently transformed for GFP expression. The dashed lines represent the background levels of isopungenin and pungenin produced in plants transiently transformed for GFP expression due to endogenous N. benthamiana glycosylation activity. Error bars represent se of results obtained with four individual plants for each of the three different transformations (PgUGT5, PgUGT5b, or GFP). For each transiently transformed plant, three pungenol-infiltrated leaves were assayed. A two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s HSD test was used to determine significant differences (P < 0.05), indicated by the use of different letters. The asterisk in C denotes that P < 0.06.