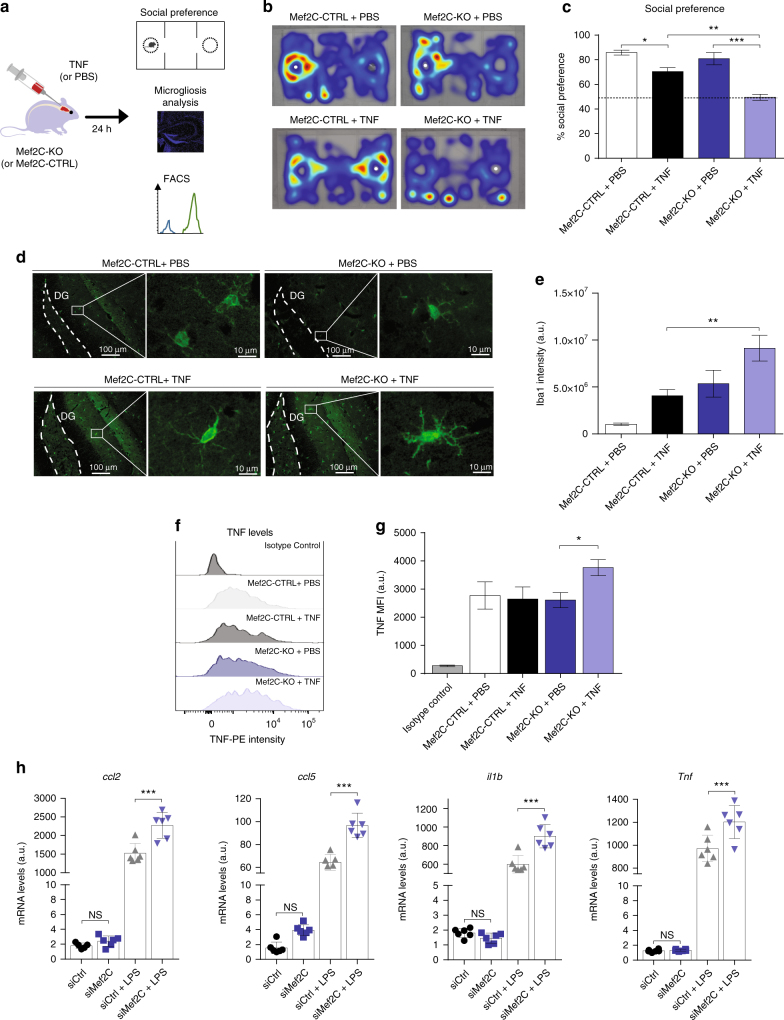
Fig. 6.
Mef2C deficiency is associated with increased pro-inflammatory response to immune stimuli. a Scheme illustrating the experimental design to determine the effects of immune challenge in Mef2C-KO mice. b, c Social preference assessed in Mef2C-KO and Mef2C-CTRL mice 24 h after intracerebroventricular injection of TNF or PBS; representative heatmaps (white dot indicates the stranger mouse location) (b) and percentage of social preference (c) (representative of two independent experiments, n = 3 per group). d, e Representative micrographs (d) and quantification (e) of Iba-1 staining in microglia in the hippocampus of Mef2C-KO and Mef2C-CTRL mice 24 h after intracerebroventricular injection of PBS or TNF. (n = 5 per group). f, g Representative histograms (f) and quantification of mean fluorescence intensity (g) of TNF staining in Mef2C-KO and Mef2C-CTRL mouse microglia 24 h after intracerebroventricular TNF or PBS administration. (n = 5 per group) h mRNA expression levels of pro-inflammatory ccl2, ccl5, il1b, Tnf in primary microglial cultures following siRNA-mediated Mef2C depletion and treatment with LPS (n = 4 per group). In all panels *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001; one-way ANOVA with Newmann–Kleus post hoc test, the results are representative of 2–3 independent experiments