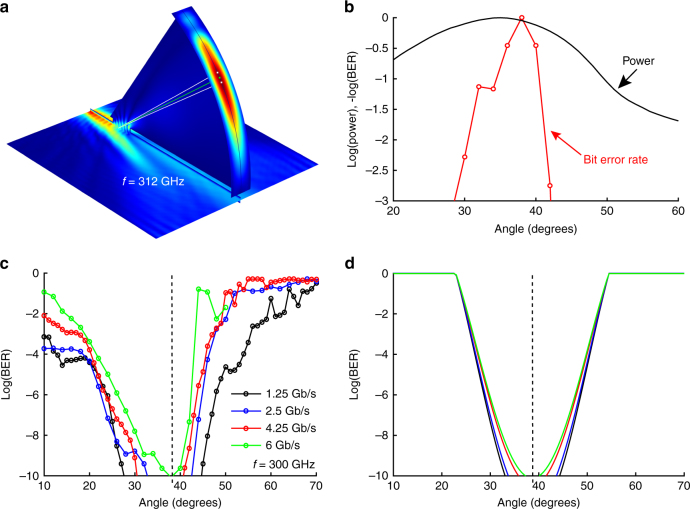
Fig. 1.
Demultiplexing of modulated THz channels for different data rates. a A 3D numerical simulation (finite element method), of a single-frequency input wave (f = 312 GHz) propagating in the waveguide (b = 0.733 mm) and then radiating into the far field through a slot in the top plate. The horizontal plane shows the intensity in a plane centered between the metal plates (i.e., inside the waveguide). The vertical (out of plane) arc shows the radiated power as a function of angle. The solid green line indicates the angle predicted by Eq. (3) for the parameters used in this simulation. The two solid white lines on either side of the green line show the predicted angles for frequencies of 302 GHz and 322 GHz, corresponding to the ±1st-order sidebands for a modulation data rate of 10 Gb/s. The angular spread of these sidebands is smaller than the angular width of the carrier wave diffracting through the slot. b Measured angular distributions for the power (black curve) and bit error rate (BER, red symbols), for an input frequency of 300 GHz and a modulation rate of 6 Gb/s. Both are normalized to unity and plotted on a log scale (BER plotted as the negative log), to facilitate comparison of the angular widths. c Measured real-time BER performance of the THz link coupled out from the slot, as a function of the angular position of the detector, for a 300 GHz carrier wave. Here, the plate separation b is 0.8 mm and slot width is 0.7 mm. Results for several different data rates all show the same optimum angle of 38.7° independent of the data rates (indicated by the vertical dashed line), though the angular width varies slightly with data rate. d A model calculation of the effect of a non-uniform angular detection sensitivity on the BER, which qualitatively reproduces the observed results. These curves assume a specific (parabolic) form for the angular detection filter, but otherwise contain no free parameters (see Supplementary Note 1 for details). In this plot, the colors correspond to the same data rates as in (c)