Figure 2. Genetic deletion of C×43 in EGCs causes inhibition of Ca2+ signaling in EGCs and reduction of the gut motor reflexes.
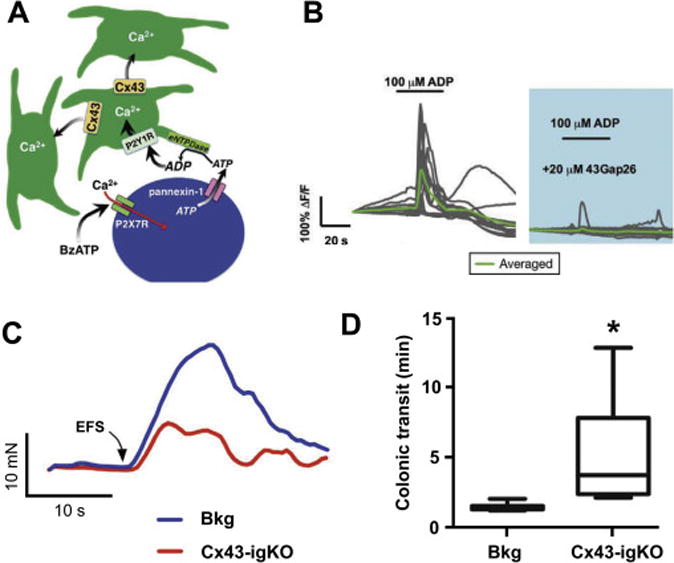
A. Model of purine-evoked Ca2+ responses through the EGC network; see text for details.
B. ADP-evoked Ca2+ responses from wild-type myenteric in situ EGCs are blocked by the connexin 43 (C×43) mimetic peptide 43Gap26, an inhibitor of the C×43 hemichannels.
C. Electrical field stimulation (EFS)-induced smooth gut muscle contractions are reduced in tamoxifen-induced glia-specific knock out of C×43 mice (C×43-igKO) and the tamoxifen treated background (Bkg) strains. Muscle relaxations were also affected (see original publication).
D. Selective genetic deletion of C×43 in EGCs increases colonic transit time, which reports on the reduction in distal colon motility in vivo. Obtained with permission for minor reformatting from [64].
