Figure 4. AKT1 was essential for AR-induced alterations in AKT/mTOR signaling, lactate formation and TNFα/IL-6 mRNA expression.
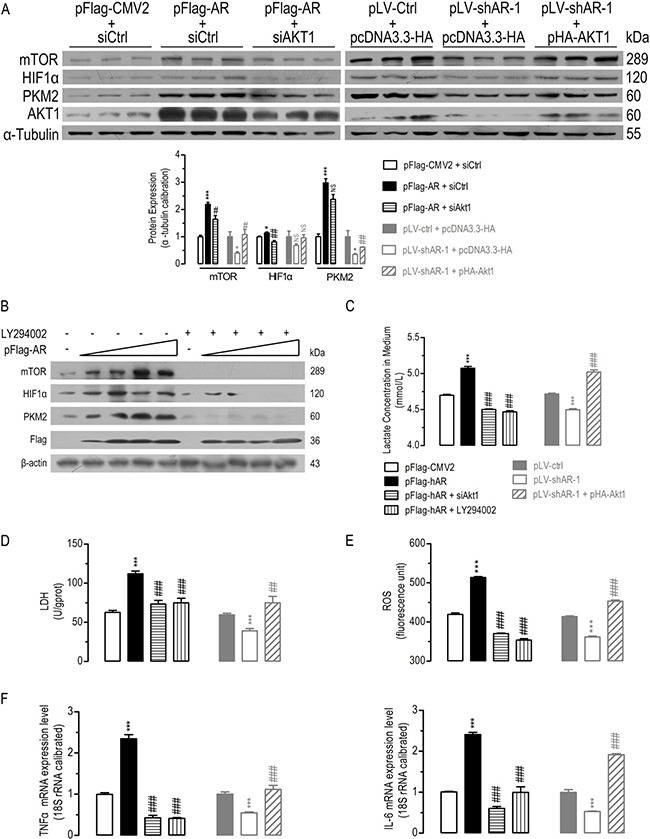
AKT1 was essential for AR-induced significantly disturbed protein expression of mTOR, HIF1a, and PKM2 in HepG2 cells (A) (n = 3). Inhibition of AKT1 phosphorylation by LY294002 significantly diminished AR overexpression-induced mTOR, HIF1α, and PKM2 protein expression (B). AKT1 was essential for AR-induced significantly disturbed lactate formation (C) (n = 6), LDH activity (D) (n = 6), ROS (E) (n = 6), TNFa/IL-6 mRNA expression (F) (n = 6) in HepG2 cells. Data were expressed as the mean ± SEM. NS, not significant; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001 (compared to pFlag-CMV2+siCtrl or pLVctrl+pcDNA3.3-HA transfected cells); #p < 0.05; ##p < 0.01; ###p < 0.001 (compared to pFlag-AR+siCtrl or pLV-shAR-1+pcDNA3.3-HA transfected cells).
