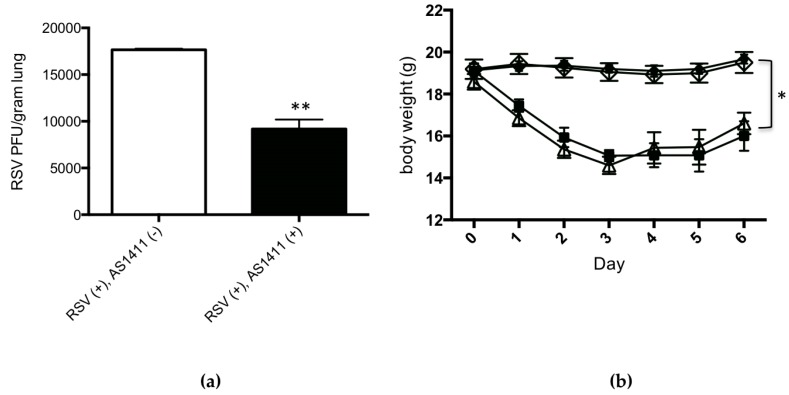
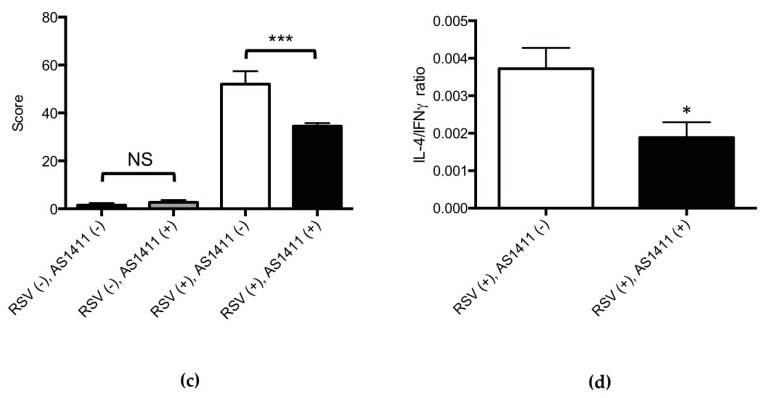
Figure 4.
In Vivo mouse data demonstrating the efficacy of AS1411 in reducing viral infection. (a) AS1411 (50 mg/kg) given intranasally one day after RSV infection reduced lung virus levels by 0.3 log (~50%) on Day 4 (Mann–Whitney U test; ** p = 0.03); (b) Similar RSV-associated drop and recovery in body weight is obtained in infected animals with or without treatment with AS1411. AS1411 had no effect on body weight in uninfected animals (* p < 0.05, 2-way ANOVA with Bonferroni procedure). Significant difference seen between sets of points is due to RSV regardless of presence of absence of AS1411. Square: RSV (+), AS1411 (+); open triangle: RSV (+), AS1411 (−); open diamond: RSV (−), AS1411 (+); circle: RSV (−). AS1411 (−); (c) AS1411 treatment decreased RSV-associated airway inflammation (*** p = 0.009; Kruskal–Wallis test with Bonferroni procedure) and did not affect airway pathology in uninfected animals (NS = not significant); (d) In RSV-infected animals, AS1411 treatment was associated with a significantly decreased IL-4/IFN-γ ratio (* p < 0.05; Mann-Whitney u test), considered to be a beneficial anti-RSV host response [36,37].