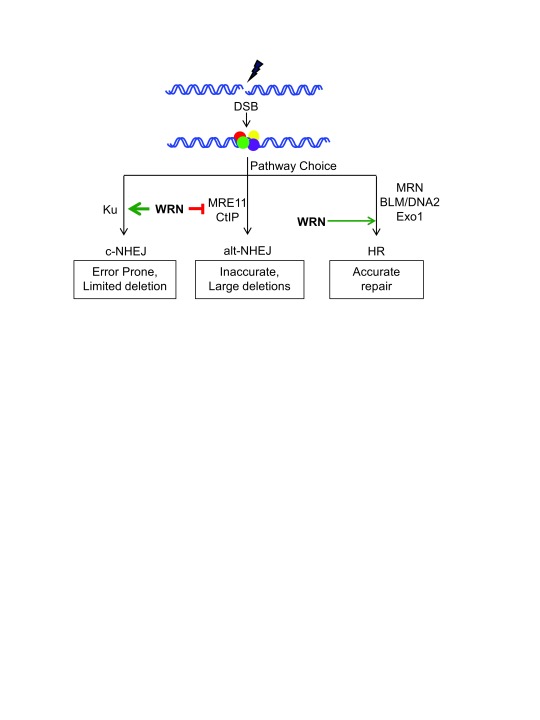
Figure 1. Double-strand break (DSB) repair pathway choice.
DSBs generated by extrinsic and intrinsic factors are recognized by the sensor proteins Ku70/Ku80, WRN, MRN, and PARP1 to mediate repair. DSBs are repaired via classical/canonical non-homologous end joining (c-NHEJ), alternative (alt)-NHEJ, and homologous recombination (HR) pathways. WRN promotes Ku-dependent c-NHEJ with its catalytic activities and strongly inhibits alt-NHEJ with its non-catalytic activities. WRN suppresses the recruitment and downstream functions of MRE11 and CtIP to inhibit alt-NHEJ. During S/G 2 phases of the cell cycle, WRN promotes HR. Accurate repair of DSBs is required for genome stability without loss of genetic information.