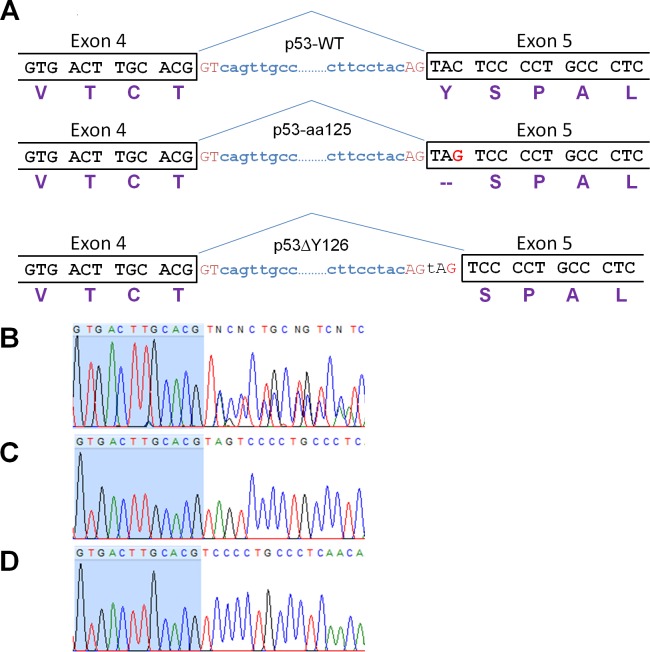
Fig 3. Sequence analysis of the 378C>G mutation in p53 protein.
(A) Schematic representation of the Exon 4-intron-Exon 5 boundaries demonstrating how the G for C substitution creates an alternative 3’splice site which, if used, eliminates the stop codon from the mutated mRNA. The three proteins are designated here as p53-WT, p53-aa125, p53ΔY126. (B) Sequence analysis of exon 4-exon 5 junction in the PCR product amplified from cDNA of EJ cells. (C, D) The representative chromatograms of the sequenced clones corresponding to p53-aa125 and p53ΔY126, respectively. The nucleotides of exon 4 are highlighted in blue. The chromatogram was generated using FinchTV software.