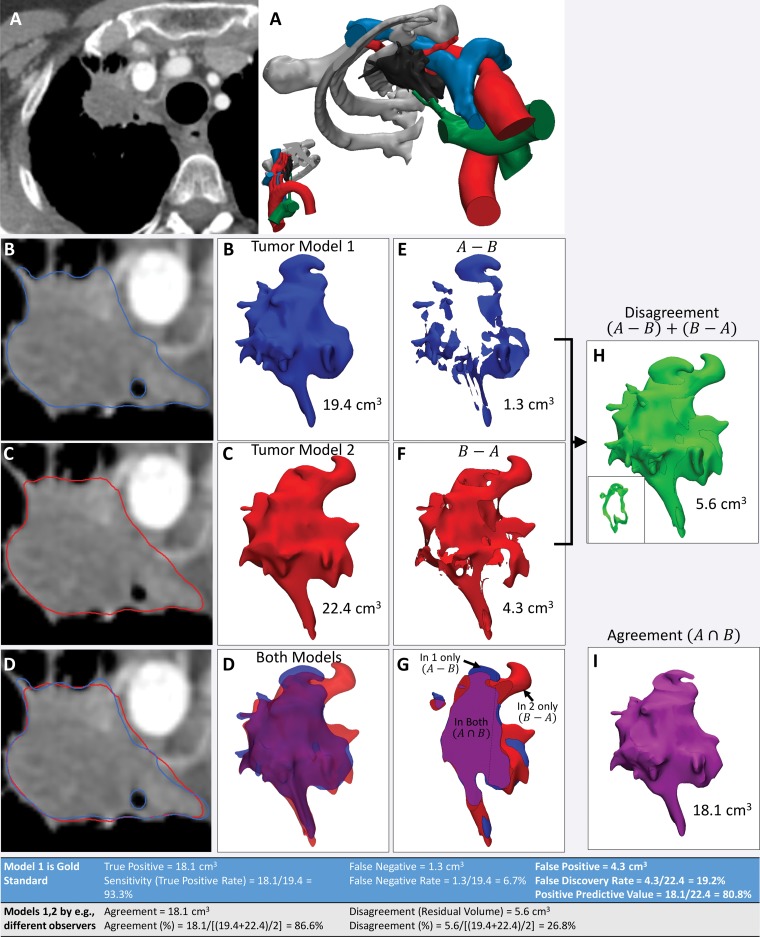
Figure 14.
Use of agreement and disagreement operations to compare different segmentation methods. A, Example assessment of similarities and differences in lung apex tumor models (right) derived from axial contrast-enhanced CT images (left). B, C, The tumor segmented by two independent readers (B and C, respectively) and seen on axial CT images (left) and 3D visualization models (right) is qualitatively different. D, Both models, seen superimposed on the axial CT image (left) and semitransparent 3D visualization models (right), are cut through the model in G. E, F, Morphologic operations are used to define differences quantitatively. For example, the model in, E, shows the tissue considered by one reader to be in the model, in disagreement with the interpretation of the second reader. The model in, F, shows the tissue considered by the second reader to be in the model, in disagreement with the interpretation of the first reader. H, I, Disagreement, H, and agreement, I, can be used to define diagnostic accuracy or reproducibility parameters (Table at bottom). The inset in, H, shows a section through the volume that it is empty where there is agreement.